英語代詞 代詞分類 代詞可分為十類,他們是:
(1)人稱
(2)物主
(3)反身
(4)相互
(5)指示
(6)疑問
(7)關係
(8)不定
(9)連線
(10)替代詞
分類 例詞
人稱代詞 主格:I我 you你 he他 she她 they他們 we我們
賓格:me我 you你 him他 her她 them他們 us我們
物主代詞 my我的 his他的 your你的(your你們的) their他們的 hers她的
指示代詞 this這 that那 these這些 those 那些
反身代詞myself我自己 himself他自己 themselves他們自己 yourself你(們)自己herself她自己
疑問代詞who誰 what什麼 which哪個
不定代詞some一些 many許多 both兩個;兩個都 any許多
關係代詞which……的物 who……的人 that……的人或物 who誰 that引導定語從句
相互代詞 each other 互相 one another互相
連線代詞 who,whom,whose,what,which,whatever,whichever,whoever,whomever
替代詞one(單數),ones(複數)
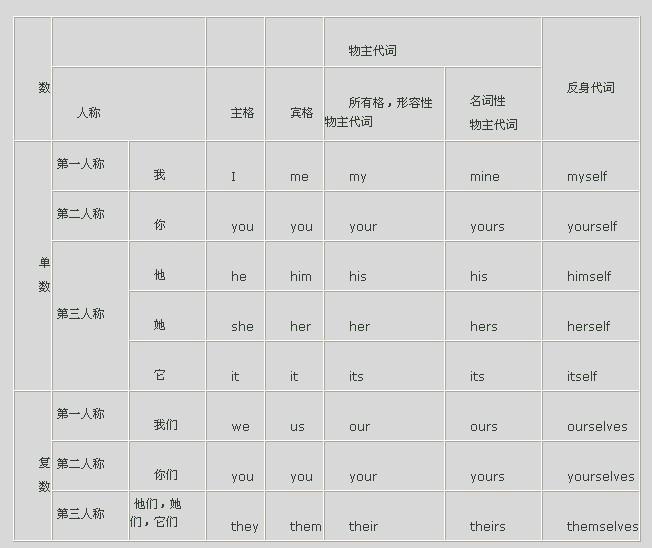
代詞用法 人稱代詞是表示"我"、"你"、"他"、"她"、"它"、"我們"、"你們"、"他們"的詞。是表示自身或人稱的代詞。
人稱代詞有人稱、數和格的變化,見下表:
單數
複數
主格
賓格
主格
賓格
第一人稱
I
me
we
us
第二人稱
you
他
he
him
they
them
她
she
her
它
it
不定
one
ones
如:He is my friend. 他是我的朋友。
It's me. 是我。
人稱代詞可用作主語,表語,賓語以及介詞賓語。
I am a worker,I work in the factory.我是一個工人,我在工廠工作。
You are a good teacher.你是一位優秀教師。
She is a little girl.她是一個小女孩。
It's a heavy box,I can't carry it.這是一個重盒子,我搬不動。
It's me. Open the door quickly.是我,快開門。
Don't tell him about it.不要告訴他這件事情。
She is always ready to help us.她隨時都在準備幫助我們。
Our teacher is very strict with us.我們的老師對我們很嚴格。
人稱代詞中幾個注意的情況:
第一人稱單數代詞 " I(我)" 不論在什麼地方都要大寫。
I study English every day.我天天學習英語。
" we " 常常代替" I "表示一種同讀者,聽眾或觀眾之間的親密關係。
We shall do our best to help the poor.我們將盡全力幫助貧困者。
" she "常常代替國家,城市,寵物等,表示一種親密或愛撫的感情。
I live in China。She is a great country.我住在中國.她是一個偉大的國家。
" it " 可指身份不清人、天氣、環境、時間。可用作形式主語、形式賓語或強調句型。
It's me. Open the door,please.是我,請開門。
" they " 有時代替一般人.
They say you are good at computer.他們說你精通計算機。
表示所有關係的代詞叫做物主代詞。物主代詞可分為形容詞性物主代詞和名詞性物主代詞兩種。列表如下。
我的
你的
他的
她的
它的
我們的
你們的
他們的
形容詞性物主代詞
my
your
his
her
its
our
your
their
名詞性物主代詞
mine
yours
hers
ours
yours
theirs
形容詞性物主代詞可用作定語,例如:
I love my country.我熱愛我的國家。
Is this your car?這是你的汽車嗎?
名詞性的物主代詞可用作主語,賓語,表語以及與"of" 連線的定語。
That car is mine,not yours.那輛汽車是我的,不是你的。
These books are ours.這些書是我們的。
Whose bag is it? It's hers.這是誰的書包? 是她的。
Yesterday I met a friend of mine in the street.昨天我在街上碰見了我的一位朋友。
表示我自己,你自己,他自己,我們自己,你們自己,他們自己等的詞叫做反身代詞。反身代詞第一,二人稱構成是由形容詞性物主代詞加 "-self " (複數加 -selves )
構成。第三人稱反身代詞是由人稱代詞賓格形式加 - self (複數加 - selves ) 構成。
第一人稱
第二人稱
第三人稱
第三人稱
第三人稱
單數
myself
yourself
himself
herself
itself
複數
ourselves
yourselves
themselves
反身代詞的用法:
反身代詞可用作賓語,表語,主語的同位語和賓語的同位語。用作同位語時表示強調"本人,自己"。
I am teaching myself computer.我自學計算機。
Take good care of yourself.把自己照顧好。
The child himself drew this picture.孩子自己畫的這張畫。
You should ask the children themselves.你應該問一問孩子們自己。
表示相互關係的代詞叫相互代詞,有each other 和one another兩組,但在運用中,這兩組詞沒什麼區別。
如:They love each other. 他們彼此相愛。
表示這個,那個,這些,那些以及it,such,same等詞叫做指示代詞。指示代詞在句中作主語,賓語,表語,定語。
That is a red car.那是一輛紅色汽車。
What do you like? I like this.你喜歡什麼? 我喜歡這個。
I should say I know that.我應該說我知道這件事情。
指示代詞的用法:
this 和 these 表示在時間上或空間上較近的人或物。
This is a book.這是一本書。
These are cars.這些是汽車。
I am busy these days.我這些日子很忙。
that 和those 表示在時間上或空間上較遠的人或物。
That is not a room.那不是一間房間。
Those are trees.那些是樹。
that 和those 還可以指前文中的事物,this 和 these 指下文中將要講到的事物。他們起一種承上或啟下的作用。
I got up late,that's why I missed the bus.我起床遲了,這就是為什麼我沒趕上汽車。
指示代詞與定
冠詞 和人稱代詞一樣,都具有指定的含義。
指示代詞分單數(this / that)和複數(these / those)兩種形式,既可作限定詞又可做代詞,例如:
單數 複數
限定詞:This girl is Mary. Those men are my teachers.
代詞: This is Mary. Those are my teachers.
表示“誰(who),誰 (whom),誰的(whose),什麼(what),哪個或哪些 (which)”等詞叫疑問代詞。
疑問代詞的用法:
疑問代詞都可用作連線代詞,引導名詞性從句(主語從句、賓語從句和表語從句)
如:Tell me who he is. 告訴我他是誰。
疑問代詞用於特殊疑問句中,疑問代詞一般放在句子的最前面,在句中可用作主語,賓語,表語,定語。
Who is here just now?剛才誰在這兒?
Whom are you looking for?你在找誰?
Whose exercise-book is this?這是誰的練習本?
What is this?這是什麼?
Which one do you like,this one or that one?你喜歡哪一個,這個還是那個?
疑問代詞還可以引導一個間接疑問句,也就是一個從句。疑問代詞在句中可用作從句的主語,賓語,表語等成分。
What we should do is still unknown.我們該乾什麼仍然還不知道。
I know whom he is looking for.我知道他在找誰。
關係代詞是用來引導定語從句的代詞。關係代詞有 who,whose,whom,that,which,as, 可用作引導從句的關聯詞,它們在句中可用作主語,表語,賓語,定語. 在主句中,它們還代表著從句所修飾的那個名詞或代詞(通稱為
先行詞 )。
This is the man who helped me yesterday.這個男人昨天幫了我。
沒有明確指定代替任何特定名詞或形容詞的詞叫做不定代詞,常用不定代詞如下:
all,any,another,both,each,every,either,few,little,many,much,no,none,neither,one,other,some以及由 some,any,no,every 和 body,one,thing 構成的複合詞。
不定代詞的用法:
不定代詞代替名詞或形容詞.在句中可用作主語,賓語,表語和定語。
Everybody should be here in time tomorrow.明天大家都要按時到。
I know nothing about it.這件事情我一點都不知道。
That's all I know.這就是我知道的。
I go to school every day.我每天去學校上學。
不定代詞的具體用法:
常見的不定代詞有all,both,each,every等,以及含有some-,any-,no-等的合成代詞,如anybody, something,no one。這些不定代詞大都可以代替名詞和形容詞,在句中作主語、賓語、表語和定語,但none和由some,any,no等構成的複合不定代詞只能作主語、賓語或表語;every和no只能作定語。如:
--- Do you have a car? --你有一輛小汽車嗎?
--- Yes,I have one. --是的,我有一輛。
--- I don't know any of them. 他們,我一個也不認識。
any:一些,任何。any 多用作否定或疑問句中,any 在句中作主語,賓語,定語。any作定語時,所修飾的名詞沒有單複數限制,一般多用複數,any 用在肯定句中,表示"任何"。
Do you have any books?你有書嗎?
You can come any time.你什麼時候都可以來。
some:一些,某些,某個。some 多用在肯定句中,表示邀請或者對方可能給予肯定回答的疑問句中等。
There are a lot of flowers in the garden,some are white,which I like very much.
花園裡有許多花,一些是白色的,我特別喜歡。
I am going to get some ink.我去弄點墨水。
Will you have some coffee,please?喝點咖啡嗎?
no:無.在句中作定語.表示否定,語氣要比 not any 強.
She knows no English.她根本就不懂英語。
I have no bike.我沒有腳踏車。
None 既可以指人也可以指物,其後通常接of短語,用作主語時,若指不可數名詞,謂語只能用單數,若指複數名詞時,則謂語可用單數(較正式),也可以用複數(非正式語體)如:
None of the milk can be used.
None of the films is/are worth seeing.
many:許多.在句中作主語,賓語,定語. many 在句中代替可數名詞。
Many of the students like English very much.許多學生非常喜歡英語。
I have many books to give you.我有許多書要給你。
much:許多。在句中作主語,賓語,定語。much 在句中代替不可數名詞。
There is not much ink in the bottle.瓶子裡沒多少墨水了。
a few,a little,few,little.:幾個,一點兒,沒幾個,沒多少。它們在句中作主語,賓語,定語,其中 a few 和 few 代替可數名詞,a little 和 little 代替不可數名詞,它們表示少量,不多,幾個,只是主觀上的一種相對說法,並沒有具體的數量標準。
Few of the books are cheap now.現在沒幾本兒書是便宜的。
A few friends came to see me yesterday.昨天有幾個朋友來看我。
I have a little money to buy the book.我的這點錢能買這本書。
There is little water in the thermos.暖水瓶沒多少水了。
連線代詞的用法連線代詞主要包括who, whom, what, which, whose, whoever, whatever, whichever, whosever 等,它們在句中可用作主語、賓語、表語、定語等,可以引導主語從句、賓語從句和表語從句,如:
I don’t know who he is. 我不知道他是誰。
What he says sounds reasonable. 他說的話聽起來有道理。
The question is who(m) we should trust. 問題是我們該信任誰。
I’ll take whoever wants to go. 誰想去我就帶誰去。
Take whichever seat you like. 你喜歡坐哪個座位就坐哪個。
I will just say whatever comes into my mind. 我想到什麼就說什麼。
【注】who, whom, whoever 等不用於名詞前作定語。
2. what 的兩種不同用法,請看以下兩個句子:
I didn’t know what he wanted. 我不知道他想要什麼。
I gave her what she wanted. 我給了她想要的一切。
上面第一句中的 what 表示“什麼”,帶有疑問的意味;第二句中的 what 表示“…所…的一切事或東西”,其意義上大致相當於 that (those) which, the thing (things) that, anything that, all that, as much as等,又如:
What [=That which] you say is quite true. 你說的完全是事實。
He saves what [= all that] he earns. 他賺多少,積蓄多少。
Call it what [= anything that] you please. 你喜歡叫它什麼就叫它什麼。這樣用的 what 有時還可後接一個名詞:He gave me what money [= all the money that] he had about him. 他把身上帶的錢全給了我。
3. 關於whatever, whoever與whichever它們可引導主語從句和賓語從句,如:
He does whatever she asks him to do. 她要他做什麼,他就做什麼。
I’ll give the ticket to whoever wants it. 誰想要這票,我就把它給誰。
Whichever team gains the most points wins. 哪個隊得分最多,哪個隊就贏。
【注】其中的 ever 主要用於加強語氣,含有“一切”、“任何”、“無論”之義。使用這類詞時,注意不要按漢語習慣用錯句子結構:任何人(誰)先來都可以得到一張票。
誤:Anyone comes first can get a ticket. / Who comes first can get a ticket
正:Anyone who comes first can get a ticket. / Whoever comes first can get a ticket.
10)替代詞:
為避免重複,在一個句子中常用替代詞替代前面已經提到過的事物。
that用來指代前文提到的可數名詞單數或者不可數名詞,表示特指,表示“一件事物”
The traffic on the main streets has a longer green signal than that on the small ones.
主要街道上的綠色交通信號比小的道路上的時間更長。
one 用來指代前文提到的可數名詞單數,表示泛指,表示“同類事物中的一個”
‘Have you got a camera?’ ‘No.’ ‘You should buy one’ (one指的是世界上任何一個照相機).
“你有照相機嗎?”“沒有。”“你應該買一架。”
This camera is great, I want to buy it.(it指的就是說話者現在看到的這一個照相機)
這個照相機很棒,我想買它。
ones用來指代前文提到的可數名詞複數,表示泛指,表示“同類事物中的一些”
Cancer cells are so radically different from normal ones that it's almost impossible to
untangle the sequence of events that made them that way.(ones指的是cells)
癌症細胞和正常細胞差異極大,要理清造成這種差異的事件的先後順序幾乎是不可能的。
While working on the new interface, Jobs would sometimes suggest what at first seemed to
be crazy ideas, but later turned out to be good ones.(ones指的是ideas)
在開發新界面的過程中,賈伯斯常常會提出一些初看起來瘋狂但之後成為好設計的意見。
the ones用來指代前文提到的可數名詞複數,表示特指,表示“這些人或這些事物”
The people who break or manipulate the rules are the ones who really become successful.
打破或操縱規則的人才是真正會成功的人。
6 reasons why your photos don't look like the ones in magazines.
為什麼你的照片看起來不像雜誌上那么好看的6個原因。
those 用來指代前文提到的可數名詞複數,表示特指,相當於the ones
Mr Zhang gave the textbooks to all the pupils except those/the ones who had already had them.
張先生把這些教科書給了所有的學生,除了那些已經有書的學生。
The products in Tanghuaseng are as good as those/the ones in Central World.
陳和盛的商品和中央世界的商品一樣好。
Studying Wendy's menu, I found that many of the items are similar to those of McDonald's.
通過研究溫迪的選單,我發現它家許多的東西都與麥當勞的相似。
the ones 和 those 的區別主要是:
1、the ones:前面可以用形容詞修飾,也可以用後置定語修飾。
例:the good ones (正確)
the ones which are good (正確)
2、 those: 前面不可以用形容詞修飾,只能用後置定語修飾。
例:good those(錯誤)
those which are good(正確)
人稱代詞 (1)人稱代詞做主語用
主格 ,做賓語、
表語 用
賓格 ,但應注意以下情況:
在
比較級 的句子中than、as後用主格、賓格都可以。
如:He is taller than me.但在下列句子中有區別。
I like Jack as much as her.=I like both Jack and her.
I like Jack as much as she.=I like Jack and she likes him,too.
(2)兩個以上的人稱代詞並列,其次序排列原則:
①在並列主語中,“I”總是放在最後,排列順序為:二三一(人稱)。
賓格 me也一樣。
You,she and I will be in charge of the case.
Mr.Zhang asked Li Hua and me to help him.
②第三人稱,男女兩性並用,男先女後。He and she still don't agree to the plan.
用法
John waited a while but eventually he went home.
約翰等了一會兒,最後他回家了。
John hoped the passenger would be Mary and indeed it was she.
約翰希望那位乘客是瑪麗,還真是她。
說明:在
複合句 中,如果主句和
從句 主語 相同,代詞主語要用在從句中,名詞主語用在主句中,例如:
When he arrived,John went straight to the bank.
約翰一到就直接去銀行了。
I saw her with them,at least,I thought it was her.
我看到她和他們在一起,至少我認為是她。(her做賓 語,them做介詞賓語,her做主語補語)
a. -- Who broke the vase? --誰打碎了花瓶?
b. -- Me. --我。(me做主語補語= It's me.)
說明:在上面兩例句中,her和me分別作主語補語。現代英語中多用
賓格 ,在正式文體中這裡應為she和I。
主賓替換 a.在簡短對話中,當人稱代詞單獨使用或在not 後,多用賓語。
---- I like English. --我喜歡英語。
---- Me too. --我也喜歡。
---- Have more wine? --再來點酒喝嗎?
---- Not me. --我可不要了。
b.在表示比較的非正式的文體中,常用賓格代替主格。但如果比較
狀語 的謂語保留,則
主語 只能用主格。
He is taller than I/me.
He is taller than I am.
a. 在
介詞 but,except 後,有時可用主格代替賓格。
b. 在電話用語中常用主格。
---- I wish to speak to Mary. --我想和瑪麗通話。
---- This is she. --我就是瑪麗。
注意:在動詞be 或to be 後的人稱代詞視其前面的名詞或代詞而定。
I thought it was she. 我以為是她。 (主格——---主格)
I thought it to be her. (
賓格 ——---賓格)
I was taken to be she. 我被當成了她。 (主格——---主格)
They took me to be her. 他們把我當成了她。 (賓格——---賓格)
指代問題 1)不定代詞 somebody,anybody,everybody,nobody,anyone, someone,everyone,no one, 及whoever和person在正式場合使用時,可用he,his,him代替。
Nobody came,did he? 誰也沒來,是嗎?
2)動物名詞的指代一般用it或they代替,有時也用he,she,帶有親切的感情色彩。
Give the cat some food. It is hungry. 給這貓一些吃的。它餓了。=Give the cat some food.She is hungry
3)指代車或國家,船舶的名詞,含感情色彩時常用she。
The Natural Day is our mother’s birthday ,I think she is very happy!
並列人稱 1) 單數人稱代詞並列作主語時,其順序為:
第二人稱 -> 第三人稱 -> 第一人稱
you -> he/she; it -> I
You,he and I should return on time.
2) 複數人稱代詞作主語時,其順序為:
第一人稱 -> 第二人稱 -> 第三人稱
we ->; you ->; They
a. 在承認錯誤,承擔責任時,
It was I and John that made her angry.
是我和約翰惹她生氣了。
b. 在長輩對晚輩,長官對下屬說話時,如長官為第一人稱, 如:I and you try to finish it.
物主代詞 1)物主代詞既有表示所屬的作用又有指代作用,例如:
John had cut his finger; apparently there was a broken glass on his desk.
約翰割破了手指,顯而易見,他桌子上有個破玻璃杯。
物主代詞 有形容詞性(my,your等)和名詞性(mine,yours等)兩種,形容詞性的物主代詞屬於
限定詞 。
名詞性的物主代詞在用法上相當於省略了中心名詞的 --'s屬格結構,例如:
Jack's cap [形容詞性物主代詞] 意為 The cap is Jack's. [名詞性物主代詞]
His cap [形容詞性物主代詞] 意為 The cap is his.[名詞性物主代詞]
a. 作主語,例如:
May I use your pen? Yours works better.
我可以用一用你的鋼筆嗎? 你的比我的好用。
b. 作賓語,例如:
I love my motherland as much as you love yours.
我愛我的祖國就像你愛你的祖國一樣深。
c. 作介詞賓語,例如:
Your should interpret what I said in my sense of the word,not in yours.
你應當按我所用的詞義去解釋我說的話,而不能按你自己的意義去解釋。
The life I have is yours. It's yours. It's yours. 我的生命屬於你,屬於你,屬於你。
雙重所有格
物主代詞 不可與 a,an,this,that,these,those,some,any,several,no,each,every,such,another,which等詞一起前置,修飾一個名詞,而必須用雙重所有格。
公式為:
a friend of mine.
each brother of his.
疑問代詞 1) 疑問代詞在句中起名詞詞組的作用,用來構成疑問句。疑問代詞有下列幾個:
指 人:who,whom,whose
指 物:what
既可指人又可指物:which
2)
疑問代詞 在句中應位於
謂語動詞 之前,沒有性和數的變化,除who之外也沒有格的變化。what,which,whose還可作
限定詞 。試比較:
疑問代詞:Whose are these books on the desk?
桌上的書是誰的?
What was the directional flow of U. S. territorial expansion?
美國的領土擴張是朝哪個方向的?
限定詞: Whose books are these on the desk?
桌上的書是誰的?
What events led to most of the east of the Mississippi River becoming part of the United States? 哪些事件使密西西比河以東的大部分土地歸屬於美國?
說明1:
無論是做
疑問代詞 還是
限定詞 ,which 和 what 所指的範圍不同。what所指的範圍是無限的,而which則指在一定的範圍內,例如:
Which girls do you like best?
你喜歡哪幾個姑娘?
What girls do you like best?
你喜歡什麼樣的姑娘?
說明2:
Whom是who的
賓格 ,在
書面語 中,它作動詞賓語或
介詞 賓語,在口語中作賓語時,可用who代替,但在介詞後只能用whom,例如:
Who(m) did you meet on the street?
你在街上遇到了誰?(作動詞賓語)
Who(m) are you taking the book to?
你要把這書帶給誰?(作介詞賓語,置句首)
To whom did you speak on the campus?
你在校園裡和誰講話了?(作
介詞 賓語,置介詞 後,不能用who取代。)
說明3:
疑問代詞 用於對介詞賓語提問時,過去的文體中介詞和疑問代詞通常一起放在句首,現代英語中,疑問代詞在句首,介詞在句末。例如:
For what do most people live and work?
大部分人生活和工作的目的是什麼?(舊文體)
What are you looking for?
說明4:
I can't make out what he is driving at.
我不知道他用意何在。
Can you tell me whose is the blue shirt on the bed?
你能告訴我床上的藍襯衣是誰的嗎?
Much of what you say I agree with,but I cannot go all the way with you.
你說的我大部分同意,但並不完全贊同。
反身代詞 反身代詞指主語與賓語為同一人或物,或表示一個動作回到該動作執行者身上時,要用反身代詞(否則就不能用反身代詞),反身代詞也可以放在名詞或代詞(主格)後面(也可以放在句尾)起強調作用。
1) 列表
I you you she he
myself yourself yourselves herself himself
we they it one
ourselves themselves itself oneself
2)做賓語
a. 有些動詞需有反身代詞
absent,bathe,amuse,blame,dry,cut,enjoy,hurt,introduce,behave
We enjoyed ourselves very much last night. 我們昨晚玩得很開心。
Please help yourself to some fish. 請你隨便吃點魚。
take pride in,be annoyed with,help oneself to sth.
I could not dress (myself) up at that time. 那個時候我不能打扮我自己。
註:有些動詞後不跟反身代詞, get up,sit-down,stand up,wake up等。
Please sit down. 請坐。
be oneself: I am not myself today. 我今天不舒服。
The thing itself is not important. 事情本身並不重要。
4) 在不強調的情況下,but,except,for 等
介詞 後賓語用反身代詞或人稱代詞
賓格 均可。如:
No one but myself (me) is hurt.
注意:
a. 反身代詞本身不能單獨作主語。
(錯) Myself drive the car.
(對) I myself drive the car. 我自己開車。
b. 但在and,or,nor連線的並列
主語 中,第二個主語可用反身代詞,特別是myself 作主語。
Charles and myself saw it.
5)第二人稱作賓語,要用反身代詞。
You should be proud of yourself. 你應為自己感到驕傲。
關係代詞 關係代詞同時起兩個作用。像其他代詞一樣,他們用作主語、表語、賓語和定語;同時像連詞一樣,它把定語從句與主句連線起來。
He said he saw me there,which was a lie.
他說在那兒看到了我,純屬謊言。
說明:關係代詞that在
從句 中作賓語或
表語 時可省略, 例如:
I've forgotten much of the Latin I once knew.
我過去懂拉丁語,現在大都忘了。
He's changed. He's not the man he was.
他變化很大,已不是過去的他了。
不定代詞 1)不定代詞有
all,both,every,each,either,neither,more,little,few,much,many,another,other,some,any,one,no 以及some,something,anything,everything,somebody,someone,anybody,anyone,nothing,nobody,no one,none,everybody,everyone.等。
2) 不定代詞的功能與用法
a. 除every 和no外不定代詞既可用作名詞,也可用作形容詞。every和no在句中只能作定語。
I have no idea about it.
b. all 都,指三者以上。
all 的主謂一致:all的單複數由它所修飾或指代的名詞的單複數決定。
All goes well. 一切進展得很好。
all 通常不與
可數名詞 單數連用,如:不說 all the book,而說 the whole book。
但all可與表時間的可數名詞單數連用,如 all day,all night,all the year; 但習慣上不說 all hour,all century。
all還可以與一些特殊的
單數 名詞連用,如 all China, all the city, all my life, all the way
3) both 都,指兩者。
a. both 與複數動詞連用,但 both… and…可與單數名詞連用。
Who can speak Japanese? We both (all) can.
4) neither 兩者都不
b. 作定語與
單數 名詞連用,但neither… nor 用作
並列連詞 ,可與
複數名詞 連用。其謂語採用就近原則。
c. 可用於下列句型,避免重複。
She can't sing,neither (can) he.
neither 與nor
d. 如前句是否定式
從句 ,則主句用neither,而不用 nor。
If you don't do it,neither should I. 如果你不乾,我也不乾。
e. 如後連續有幾個
否定句 式,則用nor,不用neither。
He can't sing,nor dance,nor skate.
5) some 某些,一些,某個
不定代詞some可以代替名詞和形容詞,常用在
肯定句 中作主語、賓語、定語等。作定語時,它可以修飾
可數名詞 (單、複數皆可)和
不可數名詞 。例如:
some are doctors,some are nurses.有些人是醫生,有些人是護士。(作主語)
6) any一些,任何
不定代詞any可以代替名詞和形容詞,常用在否定句或
疑問句 中作主語、賓語、定語等。作定語時,它可以修飾可數名詞(多為複數)和不可數名詞。例如:
there isn’t any ink in my pen.我的鋼筆沒有墨水。(作定語)
不定代詞any有時也可以用在
肯定句 中,表示"任何的"。例如:
you may come at any time;i’ll be home the whole day.你任何時候來都行,我整天都將呆在家裡。
不定代詞any也可以用作
副詞 ,做
狀語 ,表示程度。例如:
is he any better today?他今天好一點了嗎?
7)all 全體,所有(指三者以上)
all were present at the meeting.全都到會了。(作主語,代表可數名詞)
8)none 無人或無
不定代詞none的含義和all物相反,和no one,not any同義,但其用法相當於名詞,在句子中一般作主語或賓語。它代替不可數名詞作主語時,
謂語動詞 用
單數 形式;代替可數名詞作主語時,謂語動詞用單、複數皆可。例如:
none of the problems is /are easy to solve.這些問題沒有一個是容易解決的。(作主語, 代替
可數名詞 )
9) either 兩者之中的任何一個,這個或那個。
不定代詞 either 可以作主語、賓語和定語。例如:
either of them will agree to this arrangent.他們兩人中會有人同意這樣的安排的。(作主語)
10) each 每個,各自的
不定代詞each指每一個人或事物的個別情況,甚至指這些個別情況各不相同。它在句中可以作主語、賓語、定語和
同位語 。例如:
she gave the children two apples each.她給了每個小孩兩個蘋果。(作the children的同位語。)
11) every 每個,每一的,一切的
不定代詞every有"全體"的意思,和all的意義相近,但只能作定語.
none few little some
一、 none 無
1) none作主語,多與of 構成短語none of。在
答語 中,none可單獨使用。
Are there any pictures on the wall? None.
2) none作主語,
謂語動詞 單複數均可。但如做
表語 ,則其單複數與表語一致。
It is none of your business.
二、few,little 稍許,極少數
little 作主語時,謂語動詞用單數,多用於否定句。
a few,a little一些,少數
a little 作主語時,謂語動詞用單數,多用於肯定句。
三、some 一些
2) 當做"某一"解時,也可與
單數 名詞連用。(= a certain)
You will be sorry for this some day.
總有一天,你會後悔這件事的。
A certain (some) person has seen you break the rule.
某些人不同意你的看法。
注意:
(2)some用於其他句式中:
a. 肯定疑問句中:
說話人 認為對方的答案會是肯定的,或期望得到肯定回答時。
Would you like句式中,表委婉請求或建議,如:
Would you like some coffee?
If you need some help,let me know.
Some students haven't been there before.
d. 當否定的是整體中的部分時,some可用於
否定句 。如:
I haven't heard from some of my old friends these years.
這些年我沒有收到一些老朋友的信。
四、any 一些
Here are three novels. You may read any. 這有三本小說,你可任讀一本。
五、one,ones 為複數形式
ones必須和形容詞連用。如果替代的名詞時無形容詞在前,則用some,any,而不用ones。
Have you bought any rulers? Yes,I 've bought some.
one,that 和it
one表示泛指,that和it 表示特指。that與所指名詞為同類,但不是同一個,而it 與所指名詞為同一個。
I can't find my hat. I think I must buy one. (不定)
我找不到我的帽子了。我想我該去買一頂。
The hat you bought is bigger than that I bought. (同類但不同個)
你買的那頂帽子比我買的大。
I can't find my hat. I don' t know where I put it. ( 同一物)
我找不到我的帽子。我不知道我把它放在哪了。
one/another/the other
one… the other 只有兩個
some… the others 有三個以上
one… another,another…
some… others,others…
others = other people/things
the others = the rest 剩餘的全部
1) 泛指另一個用another。
2) 一定範圍內兩人(物),一個用one,另一個用the other。
3) 一定範圍內三者,一個用one,另一個用one (another),第三個可用the other,a third。
4) 一定範圍內,除去一部分人/物,剩餘的全部用the others。
5) 泛指別的人或物時,用others當在一定範圍內,除去一部分後,剩餘部分但不是全部時,也用others。
the的妙用
He is one of the students who help me.
He is the one of the students who helps me.
他是幫我的學生之一。
第二句定語從句與the one 一致。
anyone/no one/
1.anyone 和 any one
anyone僅指人,any one既可指人,也可指物。
2.no one 和none
a) none 後跟of短語,既可指人又可指物,而no one只單獨使用,只指人。
b) none 作主語,
謂語動詞 用單,複數均可,而no one作主語謂語動詞只能是
單數 。
None of you could lift it. 你們中沒有人可舉起它。
---- Did any one call me up just now? --剛才有人打電話給我嗎?
---- No one. --沒有。
3.every 和each
1) every 強調全體的概念, each強調個體概念。
Every student in our school works hard. 我們學校的學生都很用功。
Each student may have one book.. 每個學生都可有一本書。
2) every 指三個以上的人或物(含三個),each指兩個以上的人或物 (含兩個)。
3) every 只作形容詞,不可單獨使用。each可作代詞或形容詞。
Every student has to take one.
Each boy has to take one.
Each of the boys has to take one.
4) every只用作定語,each既可用作定語,也可用作主語、賓語或
同位語 。
5) every 有反覆重複的意思,如 every two weeks等; each沒有。
6) every 與not 連用,表示部分否定; each 和not連用表示全部否定。
Every man is not honest. 並非每個人都誠實。
Each man is not honest. 這兒每個人都不誠實。
both,either,neither
這些詞都可用作代詞或形容詞。其位置都在be 動詞之後,
行為動詞 之前或第一
助動詞 之後。
1) both (兩者都),either(兩者中任何一個), neither (兩者都不)。以上詞使用範圍為兩個人或物。
Neither of the two boys is clever. 兩個男孩都不聰明。
2) both,either
both與複數連用,either與單數連用。
Both the boys are clever. 兩個男孩都很聰明。
Either of the two boys is clever. 兩個男孩都很聰明。
There are flowers on both sides of the street.
(兩岸)
There are flowers on either side of the street.
(岸的兩邊)
路邊長滿了野花。
3) all (所有的,全部的人或物),any (任何一個), none (都不)。以上詞使用範圍為三者以上。
All the flowers are gone. 所有的花都謝了。
I don't like any of the flowers. 這些花我都不喜歡。
I like none of the flowers. 這些花我都不喜歡。
注意:all與none用法一樣。跟單數名詞,用單數動詞;跟
複數名詞 ,用複數動詞。
All of the students are there.
所有的學生都在那。
All (of) the milk is there.
所有的牛奶都在那。
all與whole的區別:二者都有“所有的,全部的”之意,但用法略有不同。all要置於冠詞、
物主代詞 或其他
限定詞 之前;而whole則要置於這些限定詞之後。試比較:
all my life/my whole life.
我的一生 all the world/the whole world. 全世界
many,much
How many people are there at the meeting?
How much time has we left?
Many of the workers were at the meeting.
Much of the time was spent on learning.
few,little,a few,
(a) few + 可數名詞,(a) little + 不可數名詞。
a few / a little 為肯定含義,還有一點。
few / little 為否定含義,沒有多少了。
He has a few friends. 他有幾個朋友。
He has few friends. 他幾乎沒有朋友。
We still have a little time. 我們還有點時間。
There is little time left.幾乎沒剩下什麼時間了。
典型例題:
Although he 's wealthy,he spends___ on clothes.
A. little B. few C. a little D. a few
答案:A. spend所指的是錢,不可數,只能用little或 a little. 本句為although引導的
讓步狀語從句 ,由句
意知 後句為否定含義,因此套用little表示幾乎不。
固定搭配:
only a few (=few) not a few (=many) quite a few (=many)
many a (=many)
Many books were sold.
Many a book was sold.
webwuzsdihoafd
指示代詞 表示空間或時間上遠近關係的代詞叫指示代詞。這一類詞通常是在一定的照應關係中出現,其確切含義通常取決於上下文中的照應對象或其他非語言因素,從而這一類詞在一定上下文中形成的照應關係叫做“指示照應”。
1) 指示代詞分單數(this / that)和複數(these / those)兩種形式,既可作限定詞又可做代詞,this和these一般用來指在時間或空間較近的事物或人,that和those則指時間或空間上較遠的事物或人。例如:
單數 複數
限定詞:This girl is Mary. These men are my
teachers.
代詞: This is Mary. These are my
teachers.
2) 指示代詞的句法功能;
a. 作主語
This is the way to do it.
這事兒就該這樣做。
b. 作賓語
I like this better than that.
我喜歡這個甚至那個。
c. 作主語補語
My point is this.
我的觀點就是如此。
I don't say no to that.
我並未拒絕那個。
There is no fear of that.
那並不可怕。
說明1:
指示代詞在作主語時可指物也可指人,但作其他
句子成分 時只能指物,不能指人,例如:
(對)That is my teacher. 那是我的老師。( that作主語,指人)
(對)He is going to marry this girl. 他要和這個姑娘結婚。(this作
限定詞 )
(錯)He is going to marry this. (this作賓語時不能指人)
(對)I bought this. 我買這個。(this指物,可作賓語)
說明2:
That和those可作
定語從句 的
先行詞 ,但this和 these不能,同時,在作先行詞時,只有those可指人,試比較:
(對) He admired that which looked beautiful. 他讚賞外表漂亮的東西。
(對) He admired those who looked beautiful. 他讚賞那些外表漂亮的人。(those指人)
(錯) He admired that who danced well. (that作賓語時不能指人)
(對) He admired those who danced well. 他讚賞跳舞好的人。(those指人)
(對) He admired those which looked beauti
注意事項 1、指示代詞在作
主語 時可指物也可指人,但作其他
句子成分 時只能指物,不能指人,例如:
(對)That is my teacher. 那是我的老師。( that作主語,指人)
(對)He is going to marry this girl. 他要和這個姑娘結婚。(this作
限定詞 )
(錯)He is going to marry this. (this作
賓語 時不能指人)
(對)I bought this. 我買這個。(this指物,可作賓語)
2、That和those可作
定語從句 的
先行詞 ,但this和 these不能,同時,在作先行詞時,只有those可指人,試比較:
(對) He admired that which looked beautiful. 他讚賞外表漂亮的東西。
(對) He admired those who looked beautiful. 他讚賞那些外表漂亮的人。(those指人)
(錯) He admired that who danced well. (that作賓語時不能指人)
(對) He admired those who danced well. 他讚賞跳舞好的人。(those指人)
(對) He admired those which looked beautiful. 他讚賞那些外表漂亮的東西。(those指物)
3、在回答指示代詞作
主語 的特殊問句時,如果指示代詞指人,其回答中的主語仍可以用相應的指示代詞,也可以用it或者they;但指事物時,只能用it或者they。 例如:
Who’s that? That’s/It’s Liu Dehua.那是誰?那是
劉德華 。
What are those? They are basketballs. 那些是什麼?那些是籃球。
4、在回答指示代詞作
主語 的
一般疑問句 時,不管指示代詞指人還是指物,答語中都用it或they。例如:
Is this a ruler? Yes, it is.
Are those your friends? No, they aren’t.
5、為避免重複,有時可用 that 或 those 來代替前面已提到過的人或事物;用 this 或 these 來代替下文中將要提過的人或事物。例如:
6、向別人介紹某個人時,要說“ This is ….”,而不說“ That is ….”,也不能說“ He is ….”或“ She is ….”。介紹兩個人時,先用“ This is ….”介紹一個人,然後用“ That is ….”介紹另一個人。如:
This is Li Ming. Li Ming, this is Wei Hua. 這是
李明 。李明,這是
魏華 。
This is my brother and that is my sister. 這是我哥哥,那是我妹妹。
7、one,that 和it的區別:
相互代詞 1)相互代詞只有each other和one another兩個詞組。他們表示句中動詞所敘述的動作或感覺在涉及的各個對象之間是相互存在的,例如:
It is easy to see that the people of different cultures have always copied each other.
顯而易見,不同文化的人總是相互借鑑的。
2) 相互代詞的句法功能:
a. 作動詞賓語;
People should love one another. 人們應當彼此相愛。
Does bark,cocks crow,frogs croak to each other. 吠、雞鳴、蛙兒對唱。
說明:傳統語法認為,相互關係存在於兩個人或物之間用each other, 存在於兩個以上人和物之間用one another。現代英語中,兩組詞交替使用的實例也很多,例如:
He put all the books beside each other.
他把所有書並列擺放起來。
He put all the books beside one another.
他把所有書並列擺放起來。
Usually these small groups were independent of each other.
這些小團體通常是相互獨立的。
c. 相互代詞可加-'s構成所有格,例如:
The students borrowed each other's notes.
學生們互借筆記。
3)反身代詞表示強調。
I went to see the president myself.
I went to see the president himself.
4)反身代詞不能作主語:I myself can do the work.