AVL在計算機科學中是最先發明的自平衡二叉查找樹。
基本介紹
- 中文名:AVL樹
- 外文名:AVL(Adelson-Velskii and Landis)
- 發明者: G.M. Adelson-Velsky
- 年份:1962 年
簡介
計算






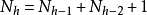

操作
y x / \ 右旋轉 (y) / \ x T3 – – – – – – – > T1 y / \ < - - - - - - - / \ T1 T2 左旋轉 (x) T2 T3
z y / \ / \ y T4 右旋轉 (z) x z / \ - - - - - - - - -> / \ / \ x T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / \ T1 T2
z y / \ / \ T1 y 左旋轉 (z) z x / \ - - - - - - - -> / \ / \ T2 x T1 T2 T3 T4 / \ T3 T4
z z x / \ / \ / \ y T4 左旋轉 (y) x T4 右旋轉 (z) y z / \ - - - - - - - - -> / \ - - - - - - - -> / \ / \T1 x y T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / \ / \ T2 T3 T1 T2
z z x / \ / \ / \ T1 y 右旋轉 (y) T1 x 左旋轉 (z) z y / \ - - - - - - - - -> / \ - - - - - - - -> / \ / \ x T4 T2 y T1 T2 T3 T4 / \ / \T2 T3 T3 T4
插入
// Recursive function to insert a key in the subtree rooted// with node and returns the new root of the subtree.struct Node* insert(struct Node* node, int key){ /* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */ if (node == NULL) return(newNode(key)); if (key < node->key) node->left = insert(node->left, key); else if (key > node->key) node->right = insert(node->right, key); else // Equal keys are not allowed in BST return node; /* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */ node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right)); /* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor node to check whether this node became unbalanced */ int balance = getBalance(node); // If this node becomes unbalanced, then // there are 4 cases // Left Left Case if (balance > 1 && key < node->left->key) return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance < -1 && key > node->right->key) return leftRotate(node); // Left Right Case if (balance > 1 && key > node->left->key) { node->left = leftRotate(node->left); return rightRotate(node); } // Right Left Case if (balance < -1 && key < node->right->key) { node->right = rightRotate(node->right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node;} 刪除
// Recursive function to delete a node with given key// from subtree with given root. It returns root of// the modified subtree.struct Node* deleteNode(struct Node* root, int key){ // STEP 1: PERFORM STANDARD BST DELETE if (root == NULL) return root; // If the key to be deleted is smaller than the // root's key, then it lies in left subtree if ( key < root->key ) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key); // If the key to be deleted is greater than the // root's key, then it lies in right subtree else if( key > root->key ) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); // if key is same as root's key, then This is // the node to be deleted else { // node with only one child or no child if( (root->left == NULL) || (root->right == NULL) ) { struct Node *temp = root->left ? root->left : root->right; // No child case if (temp == NULL) { temp = root; root = NULL; } else // One child case *root = *temp; // Copy the contents of // the non-empty child free(temp); } else { // node with two children: Get the inorder // successor (smallest in the right subtree) struct Node* temp = minValueNode(root->right); // Copy the inorder successor's data to this node root->key = temp->key; // Delete the inorder successor root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->key); } } // If the tree had only one node then return if (root == NULL) return root; // STEP 2: UPDATE HEIGHT OF THE CURRENT NODE root->height = 1 + max(height(root->left), height(root->right)); // STEP 3: GET THE BALANCE FACTOR OF THIS NODE (to // check whether this node became unbalanced) int balance = getBalance(root); // If this node becomes unbalanced, then there are 4 cases // Left Left Case if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root->left) >= 0) return rightRotate(root); // Left Right Case if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root->left) < 0) { root->left = leftRotate(root->left); return rightRotate(root); } // Right Right Case if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root->right) <= 0) return leftRotate(root); // Right Left Case if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root->right) > 0) { root->right = rightRotate(root->right); return leftRotate(root); } return root;} 