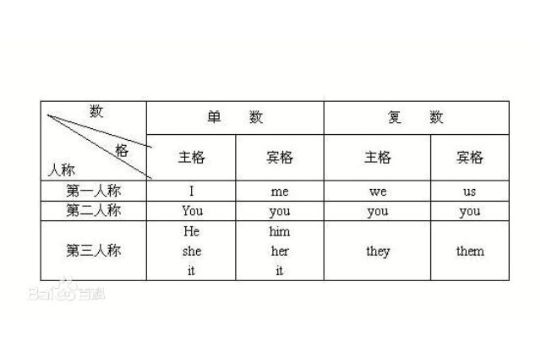
賓格(accusative case;objective case;casus accusativus)表示一個動詞直接賓語的名詞或一個前置詞的賓語。人稱代詞里的:主格放在句首做主語和表語,賓格放在句末或句中做動詞和介詞的賓語.打個比方,主人邀請賓客,主格就像主人,賓格就像賓客。主格在動詞前面,賓格在動詞或介詞後面。英語中的人稱代詞(Personal Pronouns)有主格和賓格之分,如:I, me, my ; he, him, his ; they, them,their等。顧名思義,主格(The nominative case)用作主語,賓格(The objective case)用作賓語,所有格(The possessive case)則表示所有之物。在實際運用中,主格和賓格代詞有時會混淆。
基本介紹
- 中文名:賓格
- 外文名:sb.
1.在複合結構里,人稱代詞的主格和賓格在單獨使用時,沒有問題,如很少人會犯下這樣的錯誤:
*(1)Wilcox spoke to I.
*(2)Her knew what had happened.
但在複合結構中,錯誤就難免了,如:
*(3)Wilcox spoke to my friend and I.
*(4)He and her knew what had happened.
*(5)This is between you and he.
這種錯誤是可避免的。第一,在有介詞的複合結構中,特別要注意,第二個人稱代詞,必須用賓語,如:"for you and me"和 "between Maria and him"。第二,試把複合結構中的另一部分暫時用括弧圍起來,那么該用的格就容易辨別了,如:
(7)(Marry and) he or him went downtown together.
顯然的,(6)里的代詞是賓格的"me", (7)里的代詞是主格的"he"。
2.在比較結構里,連線詞"as"或"than"後面,按理用主格式,但在口語中,人們常用賓格形式,學美式英語者,更是如此:
(8)a. You did as well as she.
b. You did as well as her.
(9)a. I am older than he.
b. I am older than him.
(a)和(b)兩種說法,都可接受。但如果"as"和"than"後頭分句的主語和詞動都要完整出現的話,這時的人稱代詞,就必須是主格,如下:
(10)You did as well as she did.
(11)I am older than he is .
此外,還有一點要注意,就是"as"和"than"後面雖然在語法上用主格好,用賓格也可,但是有時意思會有所不同。試比較(a)和(b):
(12)a. Jason praised Maria more highly than I.
b. Jason praised Maria more highly than me.
(13)a. Jason praised Maria more highly than I did (= I praised Maria).
b. Jason praised Maria more highly than he praised me.
顯然,這兩句的深層意思大有差別。遇到這種情形,為了避免誤解,不妨根據要表達的意思用完整的句式表達出來。換句話說,必要的話,要用(13)這句子。
不然,把(13)a變成(14), (13)b變成(15)也可:
(14)I did not praise Maria as highly as Jason did.
(15)Jason did not praise me as highly as he praised Maria.