光聲成像(Photoacoustic Imaging, PAI)是近年來發展起來的一種非入侵式和非電離式的新型生物醫學成像方法。當脈衝雷射照射到(熱聲成像則特指用無線電頻率的脈衝雷射進行照射)生物組織中時,組織的光吸收域將產生超聲信號,我們稱這種由光激發產生的超聲信號為光聲信號。生物組織產生的光聲信號攜帶了組織的光吸收特徵信息,通過探測光聲信號能重建出組織中的光吸收分布圖像。光聲成像結合了純光學組織成像中高選擇特性和純超聲組織成像中深穿透特性的優點,可得到高解析度和高對比度的組織圖像,從原理上避開了光散射的影響,突破了高解析度光學成像深度“軟極限”(~1 mm),可實現50 mm的深層活體內組織成像。
基本介紹
- 中文名:光聲成像
- 外文名:Photoacoustic Imaging, PAI
- 拼音:guang sheng cheng xiang
- 性質:無損醫學成像方法
- 作用:提供高解析度高對比度的組織成像
- 相關領域:醫學
1、研究套用歷史
2、光聲成像原理與系統
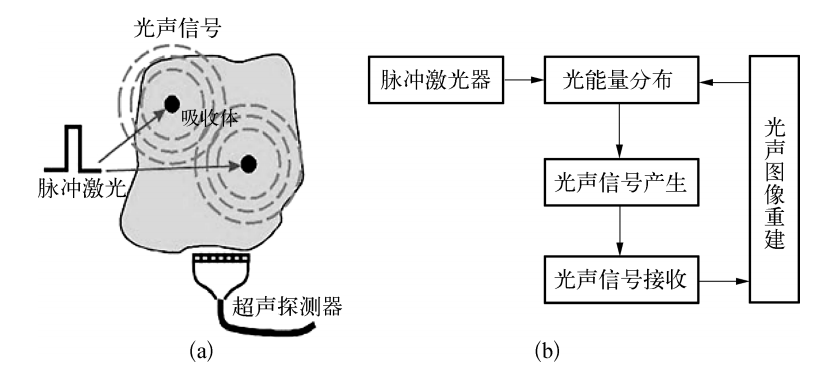
3、技術特點
4、研究分支
 圖2 光聲斷層成像系統構架圖
圖2 光聲斷層成像系統構架圖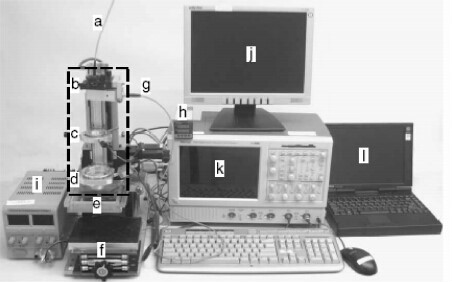
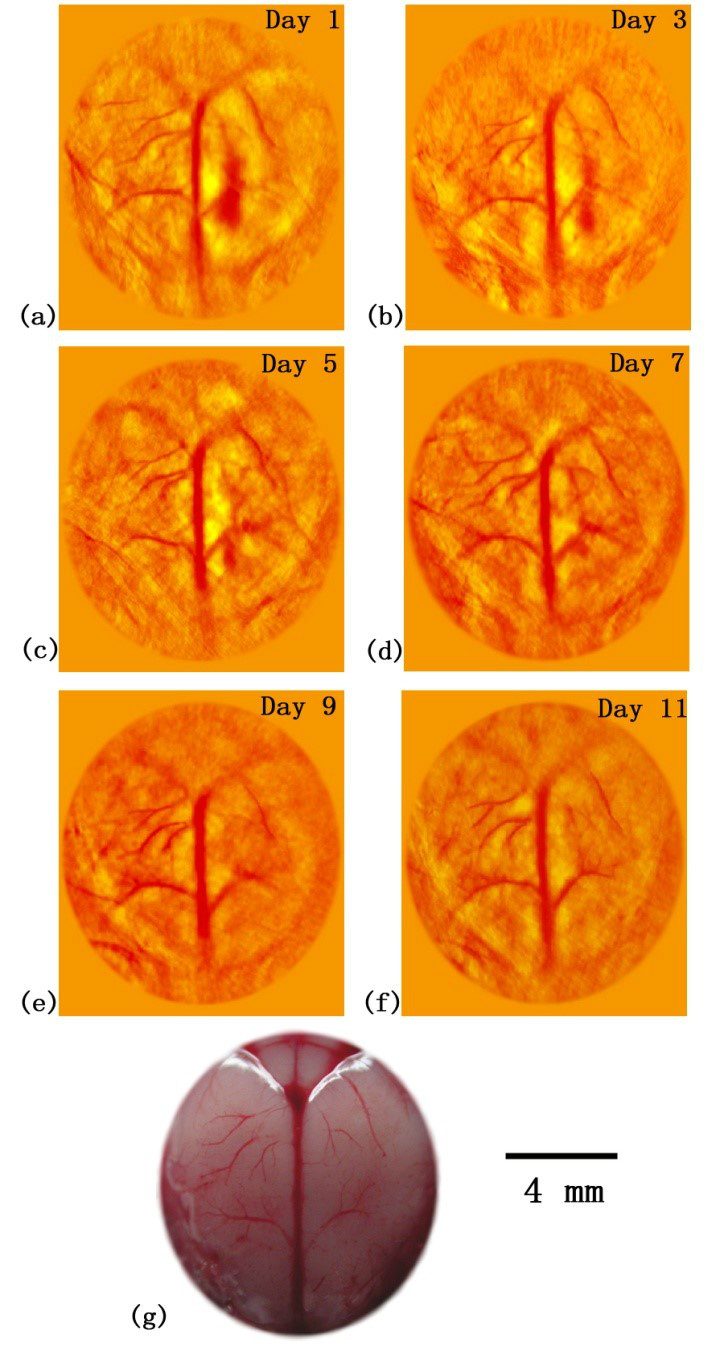
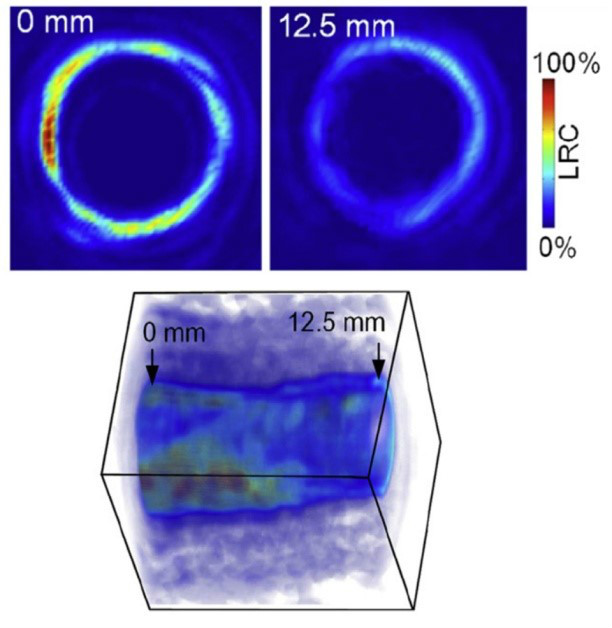
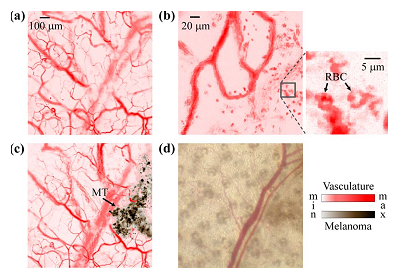

5、光聲成像套用
擴展閱讀
- 1. S. H. Yang, D. Xing, Y. Q. Lao, D. W. Yang, L. M. Zeng, L. Z. Xiang and W. R. Chen, Noninvasive monitoring of traumatic brain injury and post-traumatic rehabilitation with laser-induced photoacoustic imaging, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 243902 (2007).
- J. Zhang,S. H. Yang, X. R. Ji, Q. Zhou and D. Xing, Characterization of Lipid-Rich Aortic Plaques by Intravascular Photoacoustic Tomography: Ex Vivo and In Vivo Validation in a Rabbit Atherosclerosis Model with Histologic Correlation, J Am Col Cardiol, 64(4), 385-390, (2014).
- Y. Zhao, S. H. Yang, C. G. Chen, and D. Xing, Simultaneous optical absorption and viscoelasticity imaging based on photoacoustic lock-in measurement, Opt. Lett.,39(9), 2565, (2014).
- H. Qin, T. Zhou, S. H. Yang, Q. Chen and D. Xing, GdIII-gold nanorods for MRI and PAI dual-modality detection of macrophages in atherosclerotic inflammation, Nanomedicine,8(10), 1611-1624, (2013).
- J. P. Zhong, S. H. Yang, X. H. Zheng, T. Zhou and D. Xing, In vivo photoacoustic therapy with cancer-targeted indocyanine green-containing nanoparticles, Nanomedicine, 8(6), 903-919, (2013).
- Z. J. Chen, S. H. Yang and D. Xing, In vivo detection of hemoglobin oxygen saturation andcarboxyhemoglobin saturationwith multiwavelength photoacoustic microscopy, Opt. Lett., 37(16), 3414-3416, (2012).
- 7. S. H. Yang, F. Ye and D. Xing, Intracellular label-free gold nanorods imaging with photoacoustic microscopy, Opt. Express., 20(9), 10370, (2012).
- G. D. Gao, S. H. Yang, D. Xing, Viscoelasticity imaging of biological tissues withphase-resolved photoacoustic measurement,Opt. Lett.,36, 3341-3343, (2011).
- F. Ye, S. H. Yang and D. Xing, Three-dimensional photoacoustic imaging system in line confocal modefor breast cancer detection, Appl. Phys. Lett., 97(21), 213702, (2010).
- S. H. Yang, D. Xing, Q. Zhou, L. Z. Xiang and Y. Q. Lao, Functional imaging of cerebrovascular activities in small animalsusing high-resolution photoacoustic tomography, Med. Phys., 34(8), 3294-3301, (2007).
- H. Wang, D. Xing and L. Xiang, Photoacoustic imaging using an ultrasonic Fresnel zone plate transducer, Appl. Phys. 41 (2008).
- Y. Yuan, S. H. Yang and D. Xing, Optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy based on two dimensional scanning galvanometer, Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 0237021-3 (2012).
- B. B. Li, H. Qin, S. H. Yang and D. Xing, In vivo fast variable focus photoacoustic microscopy using an electrically tunable lens, Opt. Express., 22(17), 20130, (2014).
- X. D. Wang, Y. J. Pang, G. Ku et al. Noninvasive laser-induced photoacoustic tomography for structural and functional in vivo imaging of the brain, Nature Biotechnology, 21,803-806, (2003).
- H. F. Zhang, K. Maslov, G. Stoica et al, Functional photoacoustic microscopy for high-resolution and noninvasive in vivo imaging, Nature Biotechnol., 24, 848-851, (2006).
- Y. G. Zeng, D. Xing, Y. Wang et al, Photoacoustic and ultrasonic co-image with a linear transducer array, Opt. Lett., 29, 1760-1762, (2004).
- H. F. Zhang, K. Maslov, L. H. Wang, In vivo imaging of subcutaneous structures using functional photoacoustic microscopy, Nat. Protoc., 2, 797-804, (2007).
- G. Ku, L. V. Wang, Deeply penetrating photoacoustic tomography in biological tissues enhanced with an optical contrast agent, Opt. Lett., 30, 507-509, (2005).

