本項目致力於對2000年以來世界範圍內的主要特種移動機器人進行信息收集、數據分析和資料整理。建立的資料庫力圖對工作環境類似的移動機器人進行橫向比較,從而掌握機器人科技發展的新動向,為我院系發展特種機器人提出參考性建議,同時也促進多種機器人研究思想的融合貫通。未來還可以在已經建立的資料庫基礎上,運用系統工程、運籌學的原理,發展出輔助特種機器人設計研發的智慧型決策系統。
中國海洋大學機器人研究組 - 成員 指導老師任憑 成員蔡楊,況滿鑫 中國海洋大學機器人研究組 - 研究方法
基本介紹
- 中文名:中國海洋大學機器人研究組
- 成員:蔡楊,況滿鑫
- 研究方法:閱讀發表於機器人學主要學術會議
- 致力於:主要特種移動機器人進行信息收集
基本信息
概述
成員
研究方法
IEEEInternationalConferenceonRoboticsandAutomation
IEEE/RSJInternationalConferenceonIntelligentRobotsandSystems
ASMEInternationalDesignEngineeringTechnicalConferences;
著名學術期刊,例如:
InternationalJournalofRoboticsResearch
IEEETransactiononRobotics
ASMEJournalofMechanismsandRobotics
JournalofFieldRobots;
綜合性機器人學專著SpringerHandbookofRobotics;
中文教科書文獻以及網際網路上有影響力的科技網站。
對於收集到的信息,可以運用質量機能展開的方法進行初始分析。建立各種特種移動機器人與各種工作環境之間的對應關係。以在某一種特定環境下正常作業為目標,探索評估特種機器人機動性的質量指標。 中國海洋大學機器人研究組 - 研究成果 雙足式NameInstitution(s)Characteristics
(特徵)Operation
Environment
Locomotion
Prototype
HRP-2AISTJapan1.5mtall,58kg
bipedal,designed
foruseinhuman
environmentslike
homes,offices,and
constructionsites
Ground
Walking
HRP-2 humanoid robotHumanoidRobot
NavigationTheabilityofthesebipedalhumanoidrobotstostepoverandontoobstaclesmakesthemideallysuitedfor
environmentsdesignedforhumansGroundbipedal
walking 滑翔式NameInstitution(s)Characteristics Operation
Environment
Locomotion
Prototype
MALV1BioRobotsLLC,
USA118grams,cruising
airspeedof
approximately11
meters
persecond,surmount
obstaclesof
maximumheight
4.4centimeters
Air&GroundFlying/
Walking
/Leg-Wheel
Hybrid
118 gram MALV 1UnmannedAerialComputerVisionGroupusesabasicLucas-Kanadetrackeralgorithm,whichsendsinformationabouttheerrorbetweenthecenteroftheobjecttotrackandthecenteroftheimage,totheFuzzycontroller.SkyflyName Institution(s)CharacteristicsOperation
Environment
LocomotionPrototypeRobust
MALVBioRobotsLLC,
USA;
Universityof
Bristol;
Departmentof
Mechanical
andAerospace
Engineering,
CaseWestern
ReserveUniversityflylongdistancesAir&GroundFlying
/Walking
/Leg-Wheel
HybridRobustMALV 魚鰭式NameInstitution(s)CharacteristicsOperation
EnvironmentLocomotionPrototypeAQUAMcGill
University
andYork
University50by65by13
centimetersand
weighsapproximate
l18kilograms.Its
propulsion
isbasedonsix
flippersthatcan
providemotionin
fivedegreesoffreedomUnderwaterSwimmingAQUAMulti-DOF
Robotic
FishSchoolof
Mechanical
andAerospace
Engineering,
NanyangTechnological
Universityaslenderbody,
motorsgenerate
optimized
waveformalong
thebody
asthepropulsionUnderwater SwimmingMulti-DOF Robotic Fish 仿動物NameInstitution(s)CharacteristicsOperation
EnvironmentLocomotionPrototypeInch-
worm
RobotSchoolofMechanical
andAerospaceEngineering,
SeoulNationalUniversitymaximumvelocityof
therobotis5mm/s,
5mmperstroke,
Omegamotion,
SMAactuatorsGroundCrawlingInchworm RobotMini-
RoACHDepartmentofElectrical
Engineeringand
ComputerSciences,
Universityof
CaliforniaBerkely2.4grams,driven
byasingleDCmotor,
10bodylengths
persecondonlevel
terrainGroundWalking
/HexapedalMini-RoACHRoACHDepartmentofElectrical
Engineering
andComputerSciences,
Universityof
CaliforniaBerkely15grams,drivenbya
singleDC
motor,10bodylengths
persecondon
levelterrainGroundWalking
/HexapedalRoACHDASHDepartmentofElectrical
Engineering
andComputerSciences,
Universityof
CaliforniaBerkely16grams,drivenbya
singleDC
motor,10bodylengths
persecond
onlevelterrainGroundWalking
/HexapedalDASHiSprawlCenterforDesignResearch,
StanfordUniversity;
UniversityofPennsylvania;bio-inspired
hexapod,runsat15
body-lengthspersecond,
fastlocomotionover
roughterrain
andofexecutingrapid
turnsby
changinglegthrustanglesGroundWalking
/HexapedaliSprawlSticky-
botCenterforDesignResearch,
StanfordUniversity;
IlliniosInstitute
ofTechnologyclimbssmoothvertical
surfacessuchasglass,
plasticandceramictile
at4cm/s,
employshierarchical
compliance
,directionaladhesion
andforcecontrolGround/
Vertical
SurfaceClimbingsticybot 輪式NameInstitution(s)CharacteristicsOperationEnvironmentLocomotionPrototypeAutomatedCropYieldEstimationTheRoboticsInstituteAnautonomousorchardvehicle.Thesystemscansthebothsidesofeachtree.AcomputervisionalgorithmgroundsteerVisionGuidedMobileRobotsAutomaticControlEngineering(LSR)
AdvancedStudy(IAS)anautonomousswitching
betweentwobasic
attentionselection
mechanisms,top-downand
bottom-up,isproposed,
substitutingmanual
switchingGroundsteerpowersubstation
equipmentinspection
robotShandongJianzhuUniversityformakindoffull
monitorsystemfor
substationtogreatly
improvethesafety,
dependabilityandreality
ofthesubstation
inspectionGroundtumble
其他NameInstitution(s)CharacteristicsOperationEnvironmentLocomotionPrototypeAerobotCentreforIntelligentMachinesfullactuationtoenablesix-dofmotionandre-quirementforautonomouslocalizationairflyHybridMobileRobotTheGeorgeWashingtonUniversityThiswasaccomplishedby
integratingthelocomotionmechanismandthemanipulatorarmmechanismasoneGroundClimbingOdinchangeitsphysical
structureandbehavior
eachtimeitisreconfiguredGroundcompactmagneticwheeledrobotRoboticsandIntelligent
Systemsdoinspectionand
vibrationmeasurementsinthehousingsoflarge
generatorsandsimilar
environmentsinpower
plantsGroundClimbing/
wheeledTumblingUniversityofMinnesotatakesadvantageof
ground-bodyinteractions
toachieverichmotions
withminimalhardware
complexityGroundtumble 履帶式TrackedMobileRobottheCanadaResearchChairProgram,
theNaturalSciencesand
EngineeringResearchCouncil(NSERC),AerospaceEngineering,Ryerson
Universitylargercontactareawith
theterrain,climbing
stairs,surpassing
obstaclesornegotiating
irregularterrainGroundtracked
IEEEInternationalConferenceonRoboticsandAutomation
IEEE/RSJInternationalConferenceonIntelligentRobotsandSystems
ASMEInternationalDesignEngineeringTechnicalConferences;
著名學術期刊,例如:
InternationalJournalofRoboticsResearch
IEEETransactiononRobotics
ASMEJournalofMechanismsandRobotics
JournalofFieldRobots;
綜合性機器人學專著SpringerHandbookofRobotics;
中文教科書文獻以及網際網路上有影響力的科技網站。
對於收集到的信息,可以運用質量機能展開的方法進行初始分析。建立各種特種移動機器人與各種工作環境之間的對應關係。以在某一種特定環境下正常作業為目標,探索評估特種機器人機動性的質量指標。
研究成果
雙足式
Name | Institution(s) | Characteristics (特徵) | Operation Environment | Locomotion | Prototype |
HRP-2 | AISTJapan | 1.5mtall,58kg bipedal,designed foruseinhuman environmentslike homes,offices,and constructionsites | Ground | Walking | HRP-2 humanoid robot |
 HRP-2
HRP-2HumanoidRobot Navigation | Theabilityofthesebipedalhumanoidrobotstostepoverandontoobstaclesmakesthemideallysuitedfor environmentsdesignedforhumans | Ground | bipedal walking |
 111
111滑翔式
Name | Institution(s) | Characteristics | Operation Environment | Locomotion | Prototype |
MALV1 | BioRobotsLLC, USA | 118grams,cruising airspeedof approximately11 meters persecond,surmount obstaclesof maximumheight 4.4centimeters | Air&Ground | Flying/ Walking /Leg-Wheel Hybrid | 118 gram MALV 1 |
 118
118UnmannedAerial | ComputerVisionGroup | usesabasicLucas-Kanadetrackeralgorithm,whichsendsinformationabouttheerrorbetweenthecenteroftheobjecttotrackandthecenteroftheimage,totheFuzzycontroller. | Sky | fly |
 111
111Name | Institution(s) | Characteristics | Operation Environment | Locomotion | Prototype |
Robust MALV | BioRobotsLLC, USA; Universityof Bristol; Departmentof Mechanical andAerospace Engineering, CaseWestern ReserveUniversity | flylongdistances | Air&Ground | Flying /Walking /Leg-Wheel Hybrid | RobustMALV |
 飛行
飛行魚鰭式
Name | Institution(s) | Characteristics | Operation Environment | Locomotion | Prototype |
AQUA | McGill University andYork University | 50by65by13 centimetersand weighsapproximate l18kilograms.Its propulsion isbasedonsix flippersthatcan providemotionin fivedegreesoffreedom | Underwater | Swimming | AQUA |
 AQUA
AQUAMulti-DOF Robotic Fish | Schoolof Mechanical andAerospace Engineering, NanyangTechnological University | aslenderbody, motorsgenerate optimized waveformalong thebody asthepropulsion | Underwater | Swimming | Multi-DOF Robotic Fish |
 Multi-DOF
Multi-DOF仿動物
EnvironmentLocomotionPrototypeInch-
worm
RobotSchoolofMechanical
andAerospaceEngineering,
SeoulNationalUniversitymaximumvelocityof
therobotis5mm/s,
5mmperstroke,
Omegamotion,
SMAactuatorsGroundCrawlingInchworm RobotMini-
RoACHDepartmentofElectrical
Engineeringand
ComputerSciences,
Universityof
CaliforniaBerkely2.4grams,driven
byasingleDCmotor,
10bodylengths
persecondonlevel
terrainGroundWalking
/HexapedalMini-RoACHRoACHDepartmentofElectrical
Engineering
andComputerSciences,
Universityof
CaliforniaBerkely15grams,drivenbya
singleDC
motor,10bodylengths
persecondon
levelterrainGroundWalking
/HexapedalRoACHDASHDepartmentofElectrical
Engineering
andComputerSciences,
Universityof
CaliforniaBerkely16grams,drivenbya
singleDC
motor,10bodylengths
persecond
onlevelterrainGroundWalking
/HexapedalDASHiSprawlCenterforDesignResearch,
StanfordUniversity;
UniversityofPennsylvania;bio-inspired
hexapod,runsat15
body-lengthspersecond,
fastlocomotionover
roughterrain
andofexecutingrapid
turnsby
changinglegthrustanglesGroundWalking
/HexapedaliSprawlSticky-
botCenterforDesignResearch,
StanfordUniversity;
IlliniosInstitute
ofTechnologyclimbssmoothvertical
surfacessuchasglass,
plasticandceramictile
at4cm/s,
employshierarchical
compliance
,directionaladhesion
andforcecontrolGround/
Vertical
SurfaceClimbingsticybot 輪式
Name | Institution(s) | Characteristics | Operation Environment | Locomotion | Prototype |
Inch- worm Robot | SchoolofMechanical andAerospaceEngineering, SeoulNationalUniversity | maximumvelocityof therobotis5mm/s, 5mmperstroke, Omegamotion, SMAactuators | Ground | Crawling | Inchworm Robot |
Mini- RoACH | DepartmentofElectrical Engineeringand ComputerSciences, Universityof CaliforniaBerkely | 2.4grams,driven byasingleDCmotor, 10bodylengths persecondonlevel terrain | Ground | Walking /Hexapedal | Mini-RoACH |
RoACH | DepartmentofElectrical Engineering andComputerSciences, Universityof CaliforniaBerkely | 15grams,drivenbya singleDC motor,10bodylengths persecondon levelterrain | Ground | Walking /Hexapedal | RoACH |
DASH | DepartmentofElectrical Engineering andComputerSciences, Universityof CaliforniaBerkely | 16grams,drivenbya singleDC motor,10bodylengths persecond onlevelterrain | Ground | Walking /Hexapedal | DASH |
iSprawl | CenterforDesignResearch, StanfordUniversity; UniversityofPennsylvania; | bio-inspired hexapod,runsat15 body-lengthspersecond, fastlocomotionover roughterrain andofexecutingrapid turnsby changinglegthrustangles | Ground | Walking /Hexapedal | iSprawl |
Sticky- bot | CenterforDesignResearch, StanfordUniversity; IlliniosInstitute ofTechnology | climbssmoothvertical surfacessuchasglass, plasticandceramictile at4cm/s, employshierarchical compliance ,directionaladhesion andforcecontrol | Ground/ Vertical Surface | Climbing | sticybot |
 Inchworm
Inchworm Mini-RoACH
Mini-RoACH RoACH
RoACH DASH
DASH iSprawl
iSprawl sticybot
sticybot輪式
AdvancedStudy(IAS)anautonomousswitching
betweentwobasic
attentionselection
mechanisms,top-downand
bottom-up,isproposed,
substitutingmanual
switchingGroundsteerpowersubstation
equipmentinspection
robotShandongJianzhuUniversityformakindoffull
monitorsystemfor
substationtogreatly
improvethesafety,
dependabilityandreality
ofthesubstation
inspectionGroundtumble
其他
Name | Institution(s) | Characteristics | OperationEnvironment | Locomotion | Prototype |
AutomatedCropYieldEstimation | TheRoboticsInstitute | Anautonomousorchardvehicle.Thesystemscansthebothsidesofeachtree.Acomputervisionalgorithm | ground | steer | |
 1
1VisionGuidedMobileRobots | AutomaticControlEngineering(LSR) AdvancedStudy(IAS) | anautonomousswitching betweentwobasic attentionselection mechanisms,top-downand bottom-up,isproposed, substitutingmanual switching | Ground | steer | |
powersubstation equipmentinspection robot | ShandongJianzhuUniversity | formakindoffull monitorsystemfor substationtogreatly improvethesafety, dependabilityandreality ofthesubstation inspection | Ground | tumble |
 11
11 11
11其他
integratingthelocomotionmechanismandthemanipulatorarmmechanismasoneGroundClimbingOdinchangeitsphysical
structureandbehavior
eachtimeitisreconfiguredGroundcompactmagneticwheeledrobotRoboticsandIntelligent
Systemsdoinspectionand
vibrationmeasurementsinthehousingsoflarge
generatorsandsimilar
environmentsinpower
plantsGroundClimbing/
wheeledTumblingUniversityofMinnesotatakesadvantageof
ground-bodyinteractions
toachieverichmotions
withminimalhardware
complexityGroundtumble 履帶式TrackedMobileRobottheCanadaResearchChairProgram,
theNaturalSciencesand
EngineeringResearchCouncil(NSERC),AerospaceEngineering,Ryerson
Universitylargercontactareawith
theterrain,climbing
stairs,surpassing
obstaclesornegotiating
irregularterrainGroundtracked
Name | Institution(s) | Characteristics | OperationEnvironment | Locomotion | Prototype |
Aerobot | CentreforIntelligentMachines | fullactuationtoenablesix-dofmotionandre-quirementforautonomouslocalization | air | fly | |
HybridMobileRobot | TheGeorgeWashingtonUniversity | Thiswasaccomplishedby integratingthelocomotionmechanismandthemanipulatorarmmechanismasone | Ground | Climbing | |
 1
1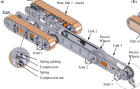 1
1Odin | changeitsphysical structureandbehavior eachtimeitisreconfigured | Ground | |||
compactmagneticwheeledrobot | RoboticsandIntelligent Systems | doinspectionand vibrationmeasurementsinthehousingsoflarge generatorsandsimilar environmentsinpower plants | Ground | Climbing/ wheeled | |
Tumbling | UniversityofMinnesota | takesadvantageof ground-bodyinteractions toachieverichmotions withminimalhardware complexity | Ground | tumble | |
 1
1 11
11 11
11履帶式
theNaturalSciencesand
EngineeringResearchCouncil(NSERC),AerospaceEngineering,Ryerson
Universitylargercontactareawith
theterrain,climbing
stairs,surpassing
obstaclesornegotiating
irregularterrainGroundtracked
TrackedMobileRobot | theCanadaResearchChairProgram, theNaturalSciencesand EngineeringResearchCouncil(NSERC),AerospaceEngineering,Ryerson University | largercontactareawith theterrain,climbing stairs,surpassing obstaclesornegotiating irregularterrain | Ground | tracked |
 11
11