基本介紹
- 中文名:順序統計樹
- 外文名:order-statistic tree
- 領域:數據結構
- 支持操作:插入、查詢、排名、選擇、刪除
- 時間複雜度:O(log n)
- 類型:一種二叉搜尋樹
簡介,選擇算法,紅黑查找樹與加權平衡樹,代碼實現,
簡介
二叉搜尋樹,是指一棵空樹或者具有下列性質的二叉樹:若任意節點的左子樹不空,則左子樹上所有節點的值均小於它的根節點的值;若任意節點的右子樹不空,則右子樹上所有節點的值均大於它的根節點的值;任意節點的左、右子樹也分別為二叉搜尋樹;沒有鍵值相等的節點。二叉搜尋樹相比於其他數據結構的優勢在於查找、插入的時間複雜度較低。為O(log n)。二叉搜尋樹是基礎性數據結構,用於構建更為抽象的數據結構,如集合、multiset、關聯數組等。順序統計樹是二叉搜尋樹的一種變體,最大的特點是能對樹中的元素進行排名和基於順序統計量對樹中的元素進行選擇,即使用選擇算法。對於樹中的每個節點,需要額外維護以這個節點為根的子樹大小(該節點下點的個數)。通過改進順序統計樹,能夠實現其他數據結構(例如, 維護節點的高度能實現AVL樹, 維護節點顏色能實現紅黑樹)。 直接使用節點大小的信息,也能實現加權平衡樹。
選擇算法
在計算機科學中,選擇算法是一種在列表或數組中找到第k個最小數字的算法;這樣的數字被稱為第k個順序統計量。該算法尋找的對象主要有三種:最小、最大和中位數。已知存在O(n)(最壞情況下為線性時間)的選擇算法,還有對於結構化數據可能有次線性的表現的算法;在極端的情況下,對於已排序數據是O(1)。選擇是一些更複雜問題的子問題,如最近鄰和最短路徑問題。 許多選擇算法是由排序算法推廣而來,反之,一些排序算法可由反覆套用選擇算法推導出來。最簡單的選擇算法是通過遍歷列表找到最小(或最大)的元素,在此過程中跟蹤當前的最小(或最大)值。這中算法與選擇排序有關。相反地,最困難的選擇算法是尋找中位數,這必然需要n/2的空間。 事實上,一個專門的中位選擇算法可用來構造一個一般選擇算法,例如中位數的中位數。已知最好的選擇算法是快速選擇(quickselect),它與快速排序有關。和快速排序類似,它有漸進最佳的複雜度,但是最壞情況的複雜度較差。不過這可以通過調整基準(pivot)的選擇來最佳化。
通過對列表或數組的排序,然後選擇所需的元素,選擇算法可以規約為排序算法。這種方法對於選擇單個元素是低效的,但需要從數組中做出很多選擇時是高效的。在這種情況下,僅僅需要一個起初一個代價昂貴的排序,緊接著就是各種便宜的選擇操作了 – 對於數組而言是 O(1)。儘管對於鍊表而言,即使排序後,選擇操作也需要 O(n),這是由於缺乏隨機訪問造成的。通常的,排序需要耗費 O(n log n) 的時間,其中n是列表的長度,儘管對於非比較算法而言可能更低一些,如基數排序和計數排序。
相比將整個列表或數組進行排序,還可以用偏排序來選擇第k小或第k大的元素。第k小的(第 k 大的) 也就是偏排序後列表中最大的 (最小的) 那個 – 這在數組中會耗費 O(1) 來訪問,在鍊表中會耗費 O(k)。
紅黑查找樹與加權平衡樹
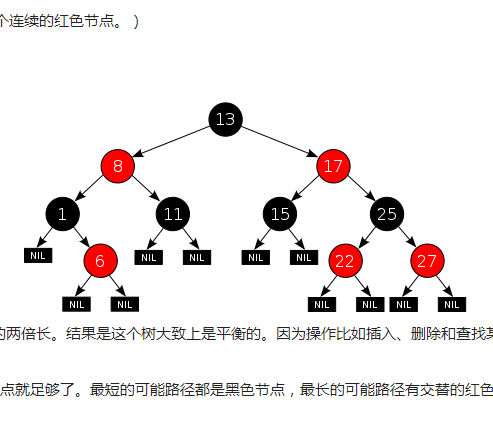
紅黑查找樹就是一種平衡的二叉查找樹。一棵二叉查找樹如果滿足下列性質,則稱為紅黑樹:
(1)每個結點或是紅色的,或是黑色的(增加一位表示顏色的存儲位);
(2)每個葉結點(空指針NIL)是黑色的;
(3)如果一個結點是紅色的,則它的兒子應是黑色的;
(4)從任一給定結點到其子孫葉結點的每條簡單路徑上都具有相同個數的黑結點。
紅黑樹和AVL樹一樣都對插入時間、刪除時間和查找時間提供了最好可能的最壞情況擔保。這不只是使它們在時間敏感的套用如實時套用(real time application)中有價值,而且使它們有在提供最壞情況擔保的其他數據結構中作為建造板塊的價值;例如,在計算幾何中使用的很多數據結構都可以基於紅黑樹。
紅黑樹是2-3-4樹的一種等同。換句話說,對於每個2-3-4樹,都存在至少一個數據元素是同樣次序的紅黑樹。在2-3-4樹上的插入和刪除操作也等同於在紅黑樹中顏色翻轉和旋轉。這使得2-3-4樹成為理解紅黑樹背後的邏輯的重要工具,這也是很多介紹算法的教科書在紅黑樹之前介紹2-3-4樹的原因,儘管2-3-4樹在實踐中不經常使用。
紅黑樹相對於AVL樹來說,犧牲了部分平衡性以換取插入/刪除操作時少量的旋轉操作,整體來說性能要優於AVL樹。
加權平衡樹是一種可以用來實現集合、字典(映射)和序列的平衡樹。這些樹結構在20世紀70年代被Nievergelt和Reingold作為有界限的自平衡樹或BB[α]樹提出。讓這些結構普及的是高德納。就像其他自平衡樹一樣,加權平衡樹儲存的賬簿信息可以在樹結構被插入和刪除操作打亂時,通過平衡結點和操作樹旋轉來使樹結構重新達到平衡。特別的地方是,加權平衡樹的每個結點儲存這個結點下子樹的大小,並且這個結點左右子樹的大小保持著某種內在聯繫。不同於AVL樹(儲存子樹的高度)和紅黑樹(儲存虛構的“顏色”位),加權平衡樹儲存記賬信息的方式是對套用真正有用的屬性:一棵樹下元素的數量等於它的根的大小,然而這個根的大小是一個用來實現順序統計樹操作的有用數據,也就是說,可以得到一個大小為n的集合下的最大元素或者決定一個順序結構下一個元素的索引。加權平衡樹在函式程式語言社區下面非常受歡迎以及被用來實現MIT Scheme的集合和映射結構還有Haskell語言的實現。
代碼實現
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <fstream>
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
enum COLOR { RED, BLACK };
struct Node {
int key;
COLOR color;
Node* p;
Node* left;
Node* right;
int size;
Node(int k, COLOR c = RED, Node* parent = nullptr, Node* l = nullptr, Node* r = nullptr,int s = 1) :key(k), color(c), p(parent), left(l), right(r),size(s) {}
};
class Tree {
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& o, const Tree& t);
private:
Node* root;
void leftR(Node* n) {
if (!n || !n->right) {
return;
}
Node* r = n->right;
Node* p = n->p;
if (p) {
if (p->right == n)
p->right = r;
else
p->left = r;
}
else
root = r;
r->p = p;
n->right = r->left;
if (n->right)
n->right->p = n;
r->left = n;
n->p = r;
//修改size值以維護
r->size = n->size;
n->size = (n->left ? n->left->size : 0) + (n->right ? n->right->size: 0) + 1;
}
void rightR(Node* n) {
if (!n || !n->left) {
return;
}
Node* l = n->left;
Node* p = n->p;
if (p) {
if (p->left == n)
p->left = l;
else
p->right = l;
}
else
root = l;
l->p = p;
n->left = l->right;
if (n->left)
n->left->p = n;
l->right = n;
n->p = l;
//修改size值以維護
l->size = n->size;
n->size = (n->left ? n->left->size : 0) + (n->right ? n->right->size : 0) + 1;
}
void keep(Node* tokeep) {
while (tokeep->p && tokeep->p->color == RED) {
if (tokeep->p->p->left == tokeep->p) {//其父為左孩子
Node* father = tokeep->p;
Node* uncle = father->p->right;
if (uncle && uncle->color == RED) {
father->color = BLACK;
uncle->color = BLACK;
father->p->color = RED;
tokeep = father->p;
}
else {
if (tokeep == father->right) {
leftR(father);
tokeep = father;
father = father->p;
}
father->color = BLACK;
father->p->color = RED;
rightR(father->p);
}
}
else {
Node* father = tokeep->p;
Node* uncle = father->p->left;
if (uncle && uncle->color == RED) {
uncle->color = BLACK;
father->color = BLACK;
father->p->color = RED;
tokeep = father->p;
}
else {
if (tokeep == father->left) {
rightR(father);
tokeep = father;
father = father->p;
}
father->color = BLACK;
father->p->color = RED;
leftR(father->p);
}
}
}
root->color = BLACK;
}
ostream& pr(ostream& o, Node* r) const {
if (!r)
return o;
o << r->key << " ";
pr(o, r->left);
pr(o, r->right);
return o;
}
ostream& mr(ostream& o, Node* r) const {
if (!r)
return o;
mr(o, r->left);
o << r->key << " ";
mr(o, r->right);
return o;
}
ostream& er(ostream& o, Node* r) const {
if (!r)
return o;
er(o, r->left);
er(o, r->right);
o << r->key << " ";
return o;
}
ostream& sr(ostream& o, Node* r)const {
if (!r)
return o;
sr(o, r->left);
o << r->size << " ";
sr(o, r->right);
return o;
}
Node* getKey(int key) const {
Node* r = root;
while (r) {
if (r->key == key)
break;
if (r->key < key)
r = r->right;
else
r = r->left;
}
if (!r)
return nullptr;
return r;
}
Node* getMin(Node* t) {
Node* res = nullptr;
while (t) {
res = t;
t = t->left;
}
return res;
}
Node* getNext(Node* t) {
if (t && t->right) {
return getMin(t->right);
}
else {
while (t && t->p && t->p->left == t) {
t = t->p;
}
if (t && t->p)
return t->p;
else
return nullptr;
}
}
void dkeep(Node* x, Node* px) {
while (x != root && (!x || x->color == BLACK)) {
if (x == px->left) {
Node* w = px->right;
if (w->color == RED) {
w->color = BLACK;
px->color = RED;
leftR(px);
w = px->right;
}
if ((!w->left || w->left->color == BLACK) && (!w->right || w->right->color == BLACK)) {
w->color = RED;
x = px;
px = px->p;
}
else {
if (!w->right || w->right->color == BLACK) {
w->color = RED;
w->left->color = BLACK;
rightR(w);
w = px->right;
}
w->color = px->color;
px->color = BLACK;
w->right->color = BLACK;
leftR(px);
x = root;
}
}
else {
Node* w = px->left;
if (w->color == RED) {
w->color = BLACK;
px->color = RED;
rightR(px);
w = px->left;
}
if ((!w->left || w->left->color == BLACK) && (!w->right || w->right->color == BLACK)) {
w->color = RED;
x = px;
px = px->p;
}
else {
if (!w->left || w->left->color == BLACK) {
w->right->color = BLACK;
w->color = RED;
leftR(w);
w = px->left;
}
w->color = px->color;
px->color = BLACK;
w->left->color = BLACK;
rightR(px);
x = root;
}
}
}
x->color = BLACK;
}
void clear(Node* root) {
if (!root)
return;
clear(root->right);
clear(root->left);
delete root;
}
int findith(Node* root,int i) const {
int l = root->left ? root->left->size:0;
int s = l + 1;
if (s == i)
return root->key;
else if (s > i)
return findith(root->left, i);
else
return findith(root->right, i - s);
}
int findth(Node* root, int key,int sum = 0) const {
if (!root)
return sum + 1;
int l = (root->left ? root->left->size : 0)+1;
if (root->key == key)
return l +sum;
if (root->key < key)
return findth(root->right, key, sum + l);
else
return findth(root->left, key, sum);
}
public:
Tree(Node* r = nullptr) :root(r) {}
void insert(int key) {
Node* tr = root;
Node* ti = nullptr;
while (tr) {
++(tr->size);
ti = tr;
if (tr->key < key)
tr = tr->right;
else
tr = tr->left;
}
if (!ti)
root = new Node(key, BLACK);
else {
Node* tokeep = new Node(key, RED, ti);
if (ti->key < key)
ti->right = tokeep;
else
ti->left = tokeep;
keep(tokeep);
}
}
bool find(int key) const {
return getKey(key) != nullptr;
}
void remove(int key) {
Node* r = getKey(key);
int color;
Node* x = nullptr;
Node* px = nullptr;
if (!r)
return;
color = r->color;
if (!r->left && !r->right) {
x = nullptr;
px = r->p;
if (!px) {
root = nullptr;
// free(r);
delete r;
return;
}
else {
if (px->left == r) {
px->left = x;
}
else {
px->right = x;
}
}
}
else if (!r->left) {
x = r->right;
px = r->p;
if (!px) {
root = x;
}
else {
if (px->right == r) {
px->right = x;
}
else {
px->left = x;
}
}
x->p = px;
}
else if (!r->right) {
x = r->left;
px = r->p;
if (!px) {
root = x;
}
else {
if (px->right == r) {
px->right = x;
}
else {
px->left = x;
}
}
x->p = px;
}
else {
Node* nr = getMin(r->right); //nr->left==nullptr
color = nr->color; // nr->p != nullptr
//修改size以維護size
nr->size = r->size;
x = nr->right;
px = nr->p;
if (px->left == nr) {
px->left = x;
}
else {
px->right = x;
}
if (x) {
x->p = px;
}
if (px == r)
px = nr;
if (!r->p) {
root = nr;
}
else if (r->p->left == r) {
r->p->left = nr;
}
else {
r->p->right = nr;
}
nr->p = r->p;
nr->left = r->left;
nr->left->p = nr;
nr->right = r->right;
if (nr->right)
nr->right->p = nr;
}
// free(r);
delete r;
//修改以維護size值
Node* tmppx = px;
while (tmppx) {
--(tmppx->size);
tmppx = tmppx->p;
}
if (color == BLACK) {
dkeep(x, px);
}
}
ostream& printsize(ostream& o) const{
mr(o,root) <<endl;
sr(o, root) << endl;
return o;
}
void clear() {
clear(root);
root = nullptr;
}
int findith(int i) const {
if (i <= 0)
return INT_MIN;
if (root->size < i)
return INT_MAX;
return findith(root, i);
}
int findth(int key) const {
return findth(root, key);
}
~Tree() {
clear();
}
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& o, const Tree &t) {
t.pr(o, t.root) << endl;
t.mr(o, t.root) << endl;
t.er(o, t.root) << endl;
return o;
}
int main() {
ifstream in("D:\\input.txt");
//istream &in=cin;
Tree t;
t.insert(1);
t.insert(2);
t.insert(3);
t.insert(4);
t.insert(8);
t.remove(8);
t.insert(7);
cout << t << endl;
t.printsize(cout);
cout << "3th\t:\t" << t.findith(2) << endl;
cout << "6\t:\t" << t.findth(0) << endl;
char c;
cin >> c;
return 0;