玫瑰果神經元是由美國艾倫腦科學研究所與匈牙利塞格德大學共同組成的科研團隊利用單細胞基因測序技術,對兩名已故中年男性捐獻的腦組織進行了研究,最終在大腦新皮層中發現的一種新型腦細胞。
基本介紹
- 中文名:玫瑰果神經元
- 外文名:Rosehip cell
- 技術:單細胞基因測序
發現經過,腦細胞介紹,研究價值,
發現經過
由美國艾倫腦科學研究所與匈牙利塞格德大學共同組成的科研團隊利用單細胞基因測序技術,對兩名已故中年男性捐獻的腦組織進行了研究,最終在大腦新皮層中發現了這種腦細胞,並根據其形狀命名為“玫瑰果神經元”。
腦細胞介紹
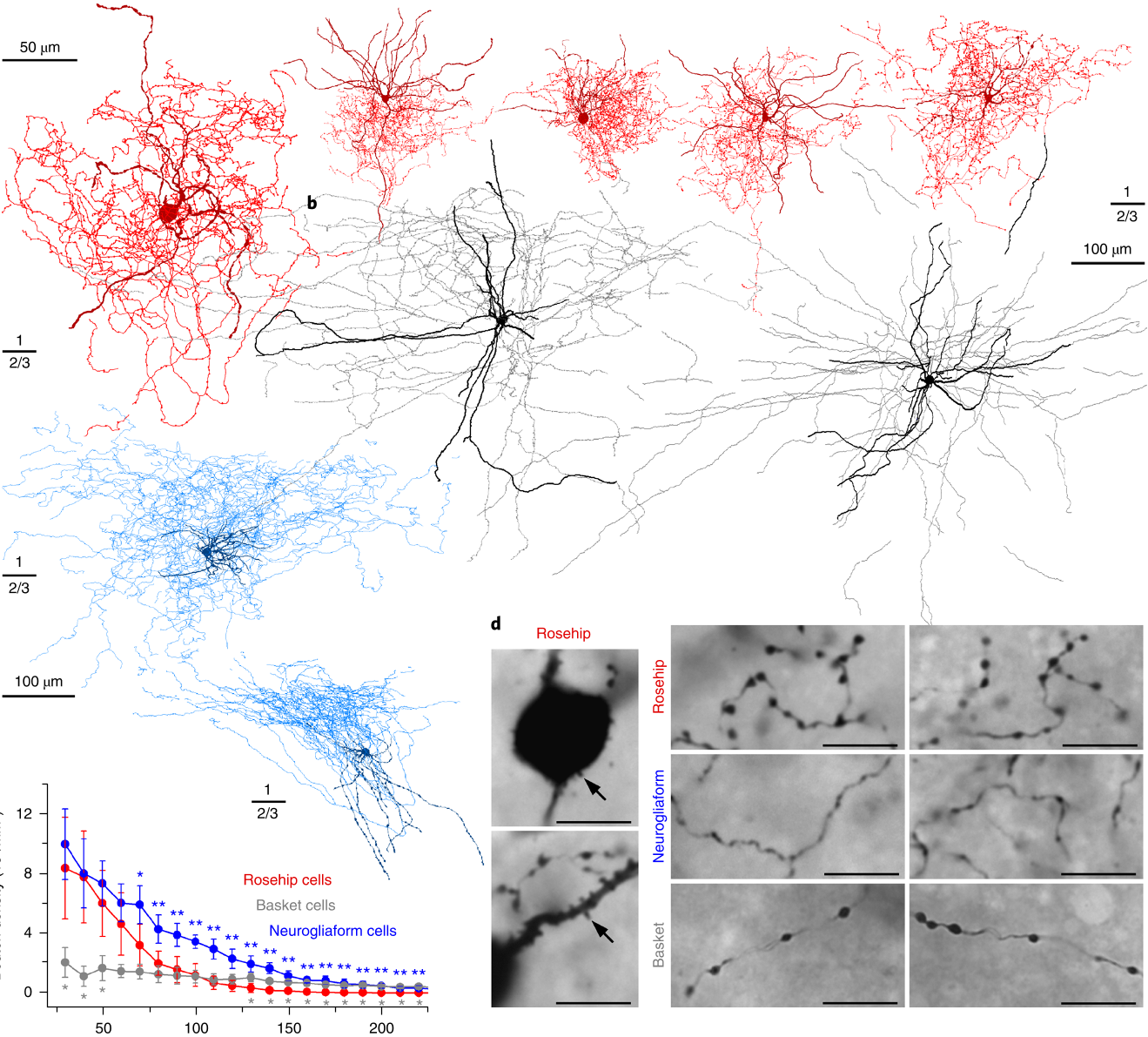
We describe convergent evidence from transcriptomics, morphology, and physiology for a specialized GABAergic neuron subtype in human cortex. Using unbiased single-nucleus RNA sequencing, we identify ten GABAergic interneuron subtypes with combinatorial gene signatures in human cortical layer 1 and characterize a group of human interneurons with anatomical features never described in rodents, having large ‘rosehip’-like axonal boutons and compact arborization. These rosehip cells show an immunohistochemical profile (GAD1+CCK+, CNR1–SST–CALB2–PVALB–) matching a single transcriptomically defined cell type whose specific molecular marker signature is not seen in mouse cortex. Rosehip cells in layer 1 make homotypic gap junctions, predominantly target apical dendritic shafts of layer 3 pyramidal neurons, and inhibit backpropagating pyramidal action potentials in microdomains of the dendritic tuft. These cells are therefore positioned for potent local control of distal dendritic computation in cortical pyramidal neurons.
(我們描述了人類皮層中特異性GABA能神經元亞型的轉錄組學,形態學和生理學的趨同證據。使用無偏的單核RNA測序,我們確定10個GABAergic中間神經元亞型人類皮質層1中的組合基因特徵,表征一組具有解剖學特徵的人類中間神經元,這些特徵從未在齧齒動物中描述,具有大的“玫瑰果”狀軸突boutons和緊密的樹枝狀結構。這些玫瑰果細胞顯示出與單個轉錄組定義的細胞類型匹配的免疫組織化學譜(GAD1 + CCK +,CNR1-SST-CALB2-PVALB-),其特異性分子標記特徵在小鼠皮質中未見。第1層中的玫瑰果細胞產生同型間隙連線,主要是第3層錐體神經元的頂端樹突軸,並抑制樹突簇的微區中的反向傳播錐體動作電位。因此,這些細胞定位用於皮質錐體神經元中遠端樹突計算的有效局部控制。)
研究價值
玫瑰果神經元細胞在小鼠等嚙齒類動物大腦中並不存在,有助於進一步揭示人腦獨特性以及為研究腦部疾病提供新線索。