基本介紹
- 中文名:歐拉函式
- 外文名:Euler's totient function
- 定義:小於n的數中與n互質的數的數目
- 發現人:歐拉(Euler)
函式內容,證明,編程實現,C++版,pascal版,C語言,Java語言,C#語言,函式表,
函式內容
通式: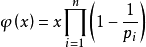
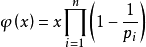
其中p1, p2……pn為x的所有質因數,x是不為0的整數。
φ(1)=1(和1互質的數(小於等於1)就是1本身)。
注意:每種質因數隻一個。 比如12=2*2*3那么φ(12)=φ(4*3)=φ(2^2*3^1)=(2^2-2^1)*(3^1-3^0)=4
若n是質數p的k次冪,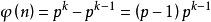 ,因為除了p的倍數外,其他數都跟n互質。
,因為除了p的倍數外,其他數都跟n互質。
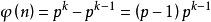
設n為正整數,以 φ(n)表示不超過n且與n互素的正整數的個數,稱為n的歐拉函式值
φ:N→N,n→φ(n)稱為歐拉函式。
歐拉函式是積性函式——若m,n互質,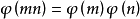
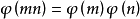
特殊性質:當n為奇質數時, , 證明與上述類似。
, 證明與上述類似。

若n為質數則

證明
若

則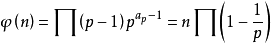
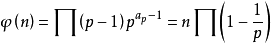
例如

與歐拉定理、費馬小定理的關係
對任何兩個互質的正整數a, m(m>=2)有

即歐拉定理
當m是質數p時,此式則為:
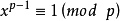
即費馬小定理。
編程實現
利用歐拉函式和它本身不同質因數的關係,用篩法計算出某個範圍內所有數的歐拉函式值。
歐拉函式和它本身不同質因數的關係:
歐拉函式ψ(N)=N{∏p|N}(1-1/p)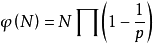
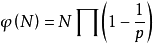
亦即: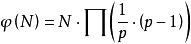 (P是數N的質因數)
(P是數N的質因數)
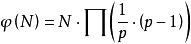
如:
ψ(10)=10×(1-1/2)×(1-1/5)=4;
ψ(30)=30×(1-1/2)×(1-1/3)×(1-1/5)=8;
ψ(49)=49×(1-1/7)= =42。
=42。

C++版
/*特性 :1.若a為質數,phi[a]=a-1;2.若a為質數,b mod a=0,phi[a*b]=phi[b]*a3.若a,b互質,phi[a*b]=phi[a]*phi[b](當a為質數時,if b mod a!=0 ,phi[a*b]=phi[a]*phi[b])*/int m[n],phi[n],p[n],nump;//m[i]標記i是否為素數,0為素數,1不為素數;p是存放素數的數組;nump是當前素數個數;phi[i]為歐拉函式int main(){ phi[1]=1; for (int i=2;i<=n;i++) { if (!m[i])//i為素數 { p[++nump]=i;//將i加入素數數組p中 phi[i]=i-1;//因為i是素數,由特性得知 } for (int j=1;j<=nump&&p[j]*i<=n;j++) //用當前已得到的素數數組p篩,篩去p[j]*i { m[p[j]*i]=1;//可以確定i*p[j]不是素數 if (i%p[j]==0) //看p[j]是否是i的約數,因為素數p[j],等於判斷i和p[j]是否互質 { phi[p[j]*i]=phi[i]*p[j]; //特性2 break; } else phi[p[j]*i]=phi[i]*(p[j]-1); //互質,特性3其,p[j]-1就是phi[p[j]] } }}pascal版
const maxn=10000; sqrtn=trunc(sqrt(maxn));var i,j,n,si:longint; fi:array[1..maxn] of longint; hash:array[1..sqrtn] of boolean; ssb:array[1..sqrtn] of longint;procedure yuchuli;var i,j,daili:longint; pd:boolean;begin fillchar(hash,sizeof(hash),false); i:=2; si:=0; while i<=sqrt(maxn) do begin if not hash[i] then begin for j:=i+1 to sqrt(ndivi) do hash[i*j]:=true; inc(si); ssb[si]:=i; end; inc(i); end; for i:=1 to maxn do fi[i]:=1; for i:=2 to maxn do begin daili:=i; for j:=1 to si do begin pd:=false; while daili mod ssb[j]=0 do begin daili:=daili div ssb[j]; if not pd then fi[i]:=fi[i]*(ssb[j]-1) else fi[i]:=fi[i]*ssb[j]; pd:=true; end; end; if daili<>1 then fi[i]:=fi[i]*(daili-1); end;end;begin yuchuli; readln(n); writeln(fi[n]);end.
C語言
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>int eular(int n){ int ret=1,i; for(i=2;i*i<=n;i++) { if(n%i==0) { n/=i,ret*=i-1; while(n%i==0) n/=i,ret*=i; } } if(n>1) ret*=n-1; return ret;}int main (){ int n,s; scanf("%d",&n); s=eular(n); printf("%d",s); return 0;}Java語言
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import java.util.Scanner;public class Oula { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in); int num=scanner.nextInt(); int a=num; double oulaAnwser=0; ArrayList<Integer> oulaList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); if (isPrime(num)){ oulaAnwser=num-1; }else{ List<Integer> allPrime = getAllPrime(num); for(int i : allPrime){ int tem=num; num=repeatdivide(num,i); if (tem!=num){ oulaList.add(i); } } oulaAnwser=a; for (int j :oulaList){ oulaAnwser=oulaAnwser*(1-(double)1/j); } } System.out.println("歐拉函式的值為"+Math.round(oulaAnwser)); } public static List<Integer> getAllPrime(int num){ ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i =2;i<num;i++){ if (isPrime(i)) { result.add(i); } } return result; } public static boolean isPrime(int num){ if(num < 2) { return false; } for(int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i++ ) { if(num%i == 0) { return false; } } return true; } public static boolean canbedivide(int num,int i ){ return num==1?false:num%i==0?true:false; } public static int repeatdivide(int num,int i ){ int result=0; if (canbedivide(num,i)){ result=repeatdivide(num/i,i); }else{ return num; } return result; }}C#語言
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;public class Program{ public static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("輸入一個整數:"); long num = long.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); long a = num; double oulaAnwser = 0; List<long> oulaList = new List<long>(); if (IsPrime(num)) { oulaAnwser = num - 1; } else { List<long> allPrime = GetAllPrime(num); foreach (long i in allPrime) { long tem = num; num = Repeatdivide(num, i); if (tem != num) { oulaList.Add(i); } } oulaAnwser = a; foreach (long j in oulaList) { oulaAnwser = oulaAnwser * (1 - (double)1 / j); } } Console.WriteLine("歐拉函式的值為" + Math.Round(oulaAnwser)); Console.ReadLine(); } public static List<long> GetAllPrime(long num) { List<long> result = new List<long>(); for (long i = 2; i < num; i++) { if (IsPrime(i)) { result.Add(i); } } return result; } public static bool IsPrime(long num) { if (num < 2) { return false; } for (long i = 2; i <= Math.Sqrt(num); i++) { if (num % i == 0) { return false; } } return true; } public static bool CanbeDivide(long num, long i) { return num == 1 ? false : num % i == 0 ? true : false; } public static long Repeatdivide(long num, long i) { long result = 0; if (CanbeDivide(num, i)) { result = Repeatdivide(num / i, i); } else { return num; } return result; }}函式表
φ(n) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
0? | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 6 |
1? | 4 | 10 | 4 | 12 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 16 | 6 | 18 |
2? | 8 | 12 | 10 | 22 | 8 | 20 | 12 | 18 | 12 | 28 |
3? | 8 | 30 | 16 | 20 | 16 | 24 | 12 | 36 | 18 | 24 |
4? | 16 | 40 | 12 | 42 | 20 | 24 | 22 | 46 | 16 | 42 |
5? | 20 | 32 | 24 | 52 | 18 | 40 | 24 | 36 | 28 | 58 |
6? | 16 | 60 | 30 | 36 | 32 | 48 | 20 | 66 | 32 | 44 |
7? | 24 | 70 | 24 | 72 | 36 | 40 | 36 | 60 | 24 | 78 |
8? | 32 | 54 | 40 | 82 | 24 | 64 | 42 | 56 | 40 | 88 |
9? | 24 | 72 | 44 | 60 | 46 | 72 | 32 | 96 | 42 | 60 |
φ(100)=40

