研究目的
對於在實際問題中出現的大型的
稀疏矩陣,若用常規分配方法在計算機中
儲存,將會產生大量的
記憶體浪費,而且在訪問和操作的時候也會造成大量時間上的浪費,為了解決這一問題,從而產生了多種解決方案。
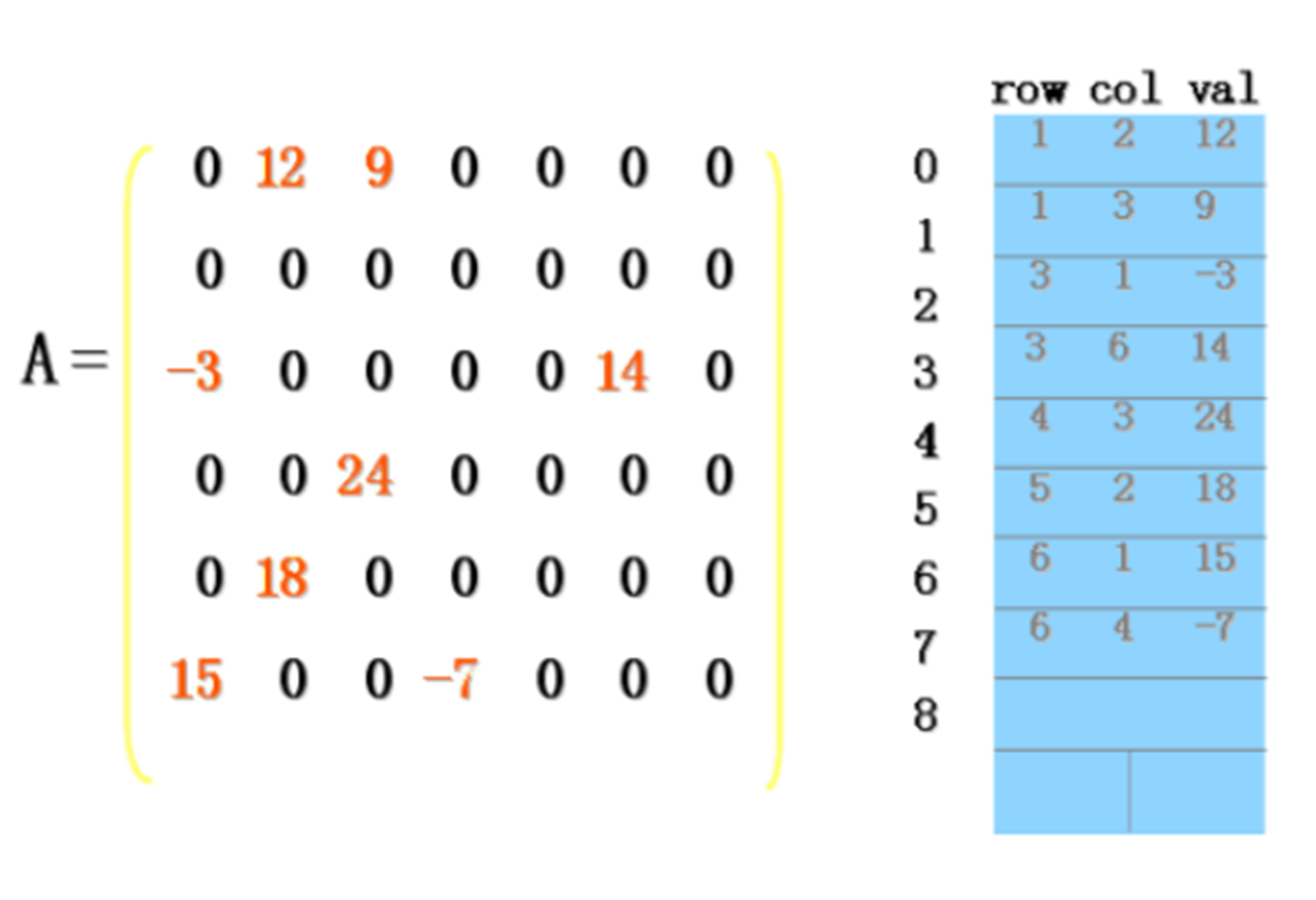
由於其自身的稀疏特性,通過壓縮可以大大節省稀疏矩陣的記憶體代價。具體操作是:將非零元素所在的行、列以及它的值構成一個三元組(i,j,v),然後再按某種規律存儲這些三元組,這種方法可以節約存儲空間。
結構描述
typedef struct{ int i ,j ; ElemType v ; }Mat; typedef struct{ int m,n,t; Mat data[MAXSIZE]; }Spmatrix; Spmatrix a,b;較完整的方式:
struct node{ int i,j; //定義三元組的行、列號 int v; //三元組的值};struct sparmatrix{ int rows,cols; //稀疏矩陣的行、列數 int terms; //稀疏矩陣的非零元個數 struct node data[maxsize]; //存放稀疏矩陣的三元組表};解釋
1、所謂“三元組”是指圖形的幾何元素構成、
圖線間的拓撲關係和尺寸約束。如果一組圖形的前二元相同而只是尺寸大小不同,則這組圖形構成一族形狀相同的系列化圖形。
2、把組成一個元素的三個數稱為三元組。一個三元組包含以下三部分的內容SDO_STARTING_OFFSET表明每個幾何元素的第一個坐標在SDO_ORDINATES數組中的存儲位置。
3、…Mt:N2)的表示稱為三元組...…Mt稱為
標號,N1、N2為結點R為關係。當n≠0時,稱Li為對結點N1的修飾。t≠0時,稱Mj為對結點N2的修飾。
求三元組合
思路
對於二元組的和等於給定值的情況, 即將數組排序後,用兩個指向數組的指針,一個從前向後掃描,一個從後向前掃描,記為first和last,當first + last == sum 則找到了一對二元組,它們的和等於sum,如果first + last < sum 則 first++, first + last > sum 則last--。同樣,三元組的情況,先將數組排序,然後固定一個元素,再去尋找一個二元組的和為sum - val,這樣就將三元組的問題,轉換成了二元組的問題。
程式
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; bool find3Numbers(int A[], int arr_size, int sum) { int l, r; /* Sort the elements */ sort(A, A + arr_size); /* Now fix the first element one by one and find the * other two elements */ for (int i = 0; i < arr_size - 2; i++) { // to find the other two elements, start two index variables //from two corners of the array and move toward each other l = i + 1; //index of the first element in the remaining elements r = arr_size - 1;//index of the last element while (l < r) { if (A[i] + A[l] + A[r] == sum) { cout << "Triplet is\t" << A[i] << "\t" << A[l] << "\t" << A[r] << endl; return true; } else if (A[i] + A[l] + A[r] < sum) { l++; } else // A[i] + A[l] + A[r] > sum { r--; } } } // If we reach here, then no triplet was found return false; } /* Driver program to test above function */ int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { int A[] = {1, 4, 45, 6, 10, 8}; int sum = 22; int arr_size = sizeof(A) / sizeof(A[0]); find3Numbers(A, arr_size, sum); return 0; }