SHA-2,名稱來自於安全散列算法2(英語:Secure Hash Algorithm 2)的縮寫,一種密碼散列函式算法標準,
基本介紹
介紹,開發,算法,
介紹
SHA-2,名稱來自於安全散列算法2(英語:Secure Hash Algorithm 2)的縮寫,一種密碼散列函式算法標準,由美國國家安全局研發,由美國國家標準與技術研究院(NIST)在2001年發布。屬於SHA算法之一,是SHA-1的後繼者。其下又可再分為六個不同的算法標準,包括了:SHA-224、SHA-256、SHA-384、SHA-512、SHA-512/224、SHA-512/256。
開發
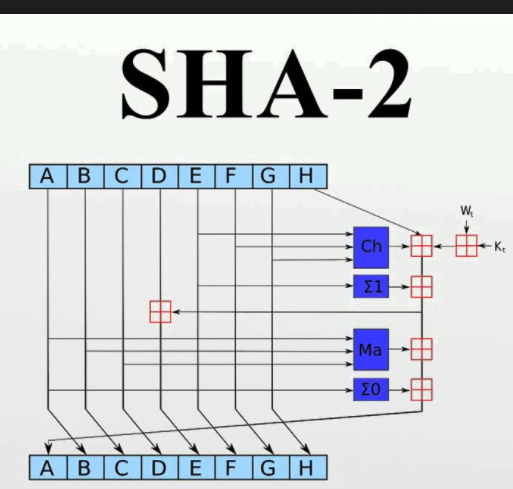
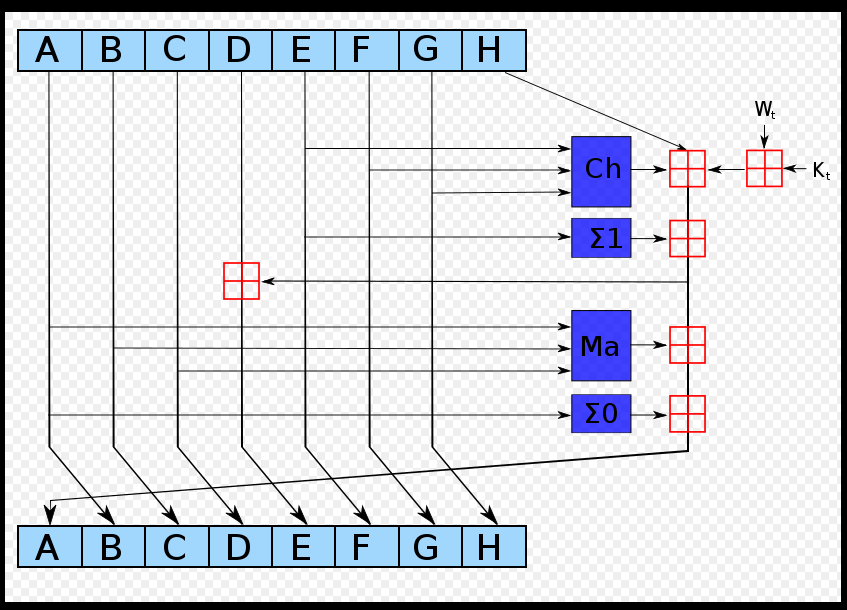
圖1所示的深藍色方塊是事先定義好的非線性函式。ABCDEFGH一開始分別是八個初始值,Kt是第t個密鑰,Wt是本區塊產生第t個word。原訊息被切成固定長度的區塊,對每一個區塊,產生n個word(n視算法而定),通過重複運作循環n次對ABCDEFGH這八個工作區塊循環加密。最後一次循環所產生的八段字元串合起來即是此區塊對應到的散列字元串。若原訊息包含數個區塊,則最後還要將這些區塊產生的散列字元串加以混合才能產生最後的散列字元串。
NIST發布了三個額外的SHA變體,這三個函式都將訊息對應到更長的訊息摘要。以它們的摘要長度(以比特計算)加在原名後面來命名:SHA-256,SHA-384和SHA-512。它們發布於2001年的FIPS PUB 180-2草稿中,隨即通過審查和評論。包含SHA-1的FIPS PUB 180-2,於2002年以官方標準發布。2004年2月,發布了一次FIPS PUB 180-2的變更通知,加入了一個額外的變種SHA-224,這是為了匹配雙密鑰3DES所需的密鑰長度而定義。
SHA-256和SHA-512是很新的散列函式,前者以定義一個word為32位,後者則定義一個word為64位。它們分別使用了不同的偏移量,或用不同的常量,然而,實際上二者結構是相同的,只在循環運行的次數上有所差異。SHA-224以及SHA-384則是前述二種散列函式的截短版,利用不同的初始值做計算。
這些新的散列函式並沒有接受像SHA-1一樣的公眾密碼社區做詳細的檢驗,所以它們的密碼安全性還不被大家廣泛的信任。Gilbert和Handschuh在2003年曾對這些新變種作過一些研究,聲稱他們沒有找到弱點。
算法
以下是SHA-256算法的偽代碼。注意,64個word w[16..63]中的比特比起SHA-1算法,混合的程度大幅提升。
Note: All variables are unsigned 32 bits and wrap modulo 2 when calculating
Initialize variables
(first 32 bits of the fractional parts of the square roots of the first 8 primes 2..19):
h0:= 0x6a09e667
h1:= 0xbb67ae85
h2:= 0x3c6ef372
h3:= 0xa54ff53a
h4:= 0x510e527f
h5:= 0x9b05688c
h6:= 0x1f83d9ab
h7:= 0x5be0cd19
Initialize table of round constants
(first 32 bits of the fractional parts of the cube roots of the first 64 primes 2..311):
k[0..63]:= 0x428a2f98, 0x71374491, 0xb5c0fbcf, 0xe9b5dba5, 0x3956c25b, 0x59f111f1, 0x923f82a4, 0xab1c5ed5, 0xd807aa98, 0x12835b01, 0x243185be, 0x550c7dc3, 0x72be5d74, 0x80deb1fe, 0x9bdc06a7, 0xc19bf174, 0xe49b69c1, 0xefbe4786, 0x0fc19dc6, 0x240ca1cc, 0x2de92c6f, 0x4a7484aa, 0x5cb0a9dc, 0x76f988da, 0x983e5152, 0xa831c66d, 0xb00327c8, 0xbf597fc7, 0xc6e00bf3, 0xd5a79147, 0x06ca6351, 0x14292967, 0x27b70a85, 0x2e1b2138, 0x4d2c6dfc, 0x53380d13, 0x650a7354, 0x766a0abb, 0x81c2c92e, 0x92722c85, 0xa2bfe8a1, 0xa81a664b, 0xc24b8b70, 0xc76c51a3, 0xd192e819, 0xd6990624, 0xf40e3585, 0x106aa070, 0x19a4c116, 0x1e376c08, 0x2748774c, 0x34b0bcb5, 0x391c0cb3, 0x4ed8aa4a, 0x5b9cca4f, 0x682e6ff3, 0x748f82ee, 0x78a5636f, 0x84c87814, 0x8cc70208, 0x90befffa, 0xa4506ceb, 0xbef9a3f7, 0xc67178f2
Pre-processing:
append the bit '1' to the message
append k bits '0', where k is the minimum number >= 0 such that the resulting message
length (in bits) is congruent to 448(mod 512)
append length of message (before pre-processing), in bits, as 64-bit big-endian integer
Process the message in successive 512-bit chunks:
break message into 512-bit chunksfor each chunk
break chunk into sixteen 32-bit big-endian words w[0..15]
Extend the sixteen 32-bit words into sixty-four 32-bit words:
for i from 16 to 63
s0:= (w[i-15] rightrotate 7) xor (w[i-15] rightrotate 18) xor(w[i-15] rightshift 3)
s1:= (w[i-2] rightrotate 17) xor (w[i-2] rightrotate 19) xor(w[i-2] rightshift 10)
w[i]:= w[i-16] + s0 + w[i-7] + s1
Initialize hash value for this chunk:
a:= h0 b:= h1 c:= h2 d:= h3 e:= h4 f:= h5 g:= h6 h:= h7
Main loop:
for i from 0 to 63
s0:= (a rightrotate 2) xor (a rightrotate 13) xor(a rightrotate 22)
maj:= (a and b) xor (a and c) xor(b and c)
t2:= s0 + maj
s1:= (e rightrotate 6) xor (e rightrotate 11) xor(e rightrotate 25)
ch:= (e and f) xor ((not e) and g)
t1:= h + s1 + ch + k[i] + w[i]
h:= g g:= f f:= e e:= d + t1 d:= c c:= b b:= a a:= t1 + t2
Add this chunk's hash to result so far:
h0:= h0 + a h1:= h1 + b h2:= h2 + c h3:= h3 + d h4:= h4 + e h5:= h5 + f h6:= h6 + g h7:= h7 + h
Produce the final hash value (big-endian):digest = hash = h0 append h1 append h2 append h3 append h4 append h5 append h6 append h7
其中ch函式及maj函式可利用前述SHA-1的最佳化方式改寫。
SHA-224和SHA-256基本上是相同的,除了:
- h0到h7的初始值不同,以及
- SHA-224輸出時截掉h7的函式值。
SHA-512和SHA-256的結構相同,但:
- SHA-512所有的數字都是64位,
- SHA-512運行80次加密循環而非64次,
- SHA-512初始值和常量拉長成64位,以及
- 二者比特的偏移量和循環位移量不同。
SHA-384和SHA-512基本上是相同的,除了:
- h0到h7的初始值不同,以及
- SHA-384輸出時截掉h6和h7的函式值。