電阻抗斷層成像(Electrical Impedance Tomography,EIT)重構算法的目的是通過電流激勵區域邊界上的電壓值重構出區域內部的電阻抗分布。重構算法一般分為兩種,一種是重構出電阻抗絕對值的靜態算法,一種是重構出電阻抗相對變化值的動態算法。由於測量數、邊界形狀等一系列實際條件的限制,重構圖像只能給出一個真實電阻抗的估計。
基本介紹
- 中文名:電阻抗斷層成像
- 外文名:Electrical Impedance Tomography,EIT
1.正問題,2.逆問題,3.逆問題正則化,4.算法分類,擴展閱讀,
1.正問題
生物體的電磁場規律都可以用麥克斯韋(Maxwell)方程組表示:
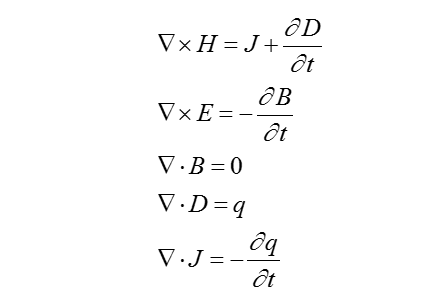
其中,  為矢量微分運算元(泊松運算元),E為電場強度,D為電感應強度,B為磁感應強度,H為磁場強度,J為傳導電流密度。電、磁場中的場量E、B與D、H之間的關係由媒質的特性決定,在各向同性的媒質中,它們有如下關係:
為矢量微分運算元(泊松運算元),E為電場強度,D為電感應強度,B為磁感應強度,H為磁場強度,J為傳導電流密度。電、磁場中的場量E、B與D、H之間的關係由媒質的特性決定,在各向同性的媒質中,它們有如下關係:




其中,ε為復介電常數;μ為導磁率;γ為電導率。在我們所觀察的電流場中,沒有孤立電荷存在,因而電荷密度為0,在較低頻率下,可以忽略介電常數的影響,又因成像目標內部無自由電荷,從而得到以下方程(拉普拉斯方程):
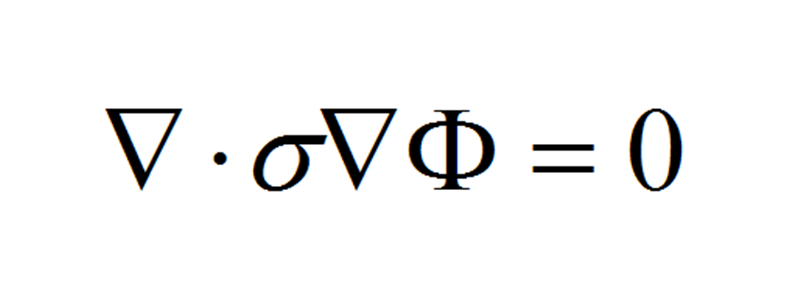
其中,σ為純電導率,對應的邊界條件為:

在進行EIT正問題分析時,可以將區域Ω分為許多離散的單元,每個小單元內有一個均勻電阻抗的分布,可以得到離散域的一個線性化的等式,以矩陣的形式寫為:

其中, 是測量電壓變化值矢量,
是測量電壓變化值矢量, 是離散電阻抗變化矢量,S是敏感係數矩陣,其中的係數可以表示為:
是離散電阻抗變化矢量,S是敏感係數矩陣,其中的係數可以表示為:



其中i代表第i個驅動測量對,j代表第j個單元,積分則是對單元容積的積分。
2.逆問題
建立EIT正問題後,可以將EIT圖像描述看成一個逆問題的求解,即已知激勵電流和邊界電壓求解內部電阻抗變化。我們就可以通過對敏感矩陣進行求逆來獲得電阻抗變化的分布 ,因此有:
,因此有:


給定邊界測量值 ,我們可以計算擾動的電阻抗圖像
,我們可以計算擾動的電阻抗圖像 。這個結果對任何維數和電極安排都是有效的,但是電極的位置和電極對的驅動測量方式都會影響到敏感矩陣的形式以及矩陣逆的穩定性,進一步影響圖像的重構質量。
。這個結果對任何維數和電極安排都是有效的,但是電極的位置和電極對的驅動測量方式都會影響到敏感矩陣的形式以及矩陣逆的穩定性,進一步影響圖像的重構質量。


3.逆問題正則化
針對線性離散正問題,我們假設不含噪聲的理想狀態下:

其中V為測量值向量,大小為M, 為未知的模型參數向量,大小為N,S為敏感矩陣,大小為(M×N)。在EIT的研究中,ν指邊界電壓測量值的變化量,為內部電阻抗的變化量,S其為敏感矩陣,其逆問題可表示為:
為未知的模型參數向量,大小為N,S為敏感矩陣,大小為(M×N)。在EIT的研究中,ν指邊界電壓測量值的變化量,為內部電阻抗的變化量,S其為敏感矩陣,其逆問題可表示為:


其中 為S的逆,在大多數情況下,測量值通常只能在連續域的幾個獨立點上進行測量獲得,而模型參數理論上講在域內有無窮多個,因此可以認為M<N,逆問題是非適定的。這種情況下,方程有無窮多個解,可以說有無窮多種模型參數在一定的精度要求下是可以滿足測量數據的,為了克服這個問題,逆問題的求解就必須進行正則化。
為S的逆,在大多數情況下,測量值通常只能在連續域的幾個獨立點上進行測量獲得,而模型參數理論上講在域內有無窮多個,因此可以認為M<N,逆問題是非適定的。這種情況下,方程有無窮多個解,可以說有無窮多種模型參數在一定的精度要求下是可以滿足測量數據的,為了克服這個問題,逆問題的求解就必須進行正則化。

採用Tikhonov正則化的解如下:
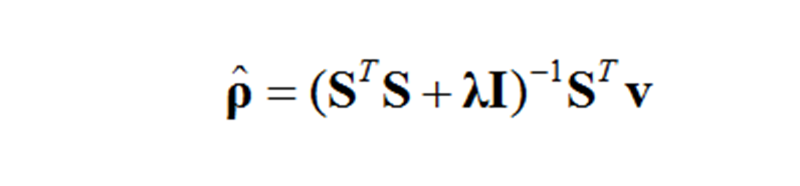
其中,λ為正則化參數
4.算法分類
世界各研究小組對EIT的圖像重建算法進行了廣泛的研究,各式各樣新穎的重構算法相繼被提出,一種算法分類如圖1所示:
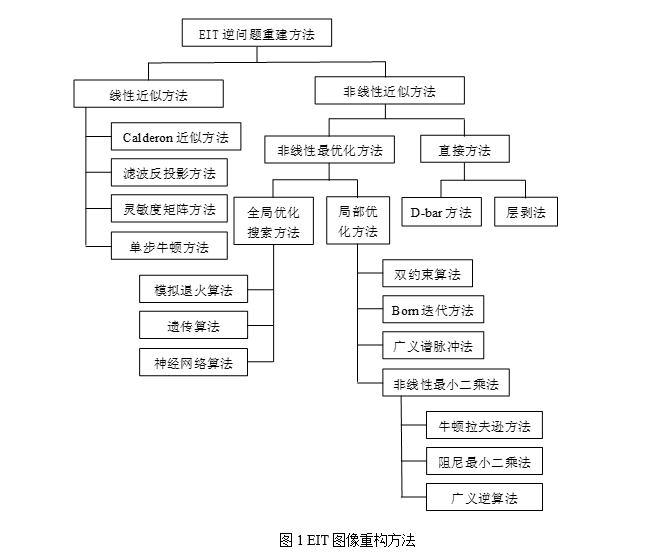
圖1 EIT圖像重構方法
擴展閱讀
[1] BH Brown and DC Barber. ‘Applied potential tomography’ – a new in-vivo medical imaging technique. [J]. Proc. of the HPA Ann. Conf., Sheffield, 1982.
[2] T Murai and Y Kagawa. Electrical impedance computed tomography based on a finite element model. [J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1985, 32(3):177-184.
[3] M Cheney and D Isaacson. NOSER: An algorithm for solving the inverse conductivity problem. [J]. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 1990, 2(2):66-75.
[4] A Adler and R Guardo. A neural network image reconstruction technique for electrical impedance tomography. [J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1994, 13(4):594-600.
[5] CJ Kotre. EIT image reconstruction using sensitivity weighted filtered backprojection. [J]. Phys. Meas., 1994, 15:125-136.
[6] A Adler and R Guardo. Electrical impedance tomography: regularized imaging and contrast detection. [J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1996, 15(2): 170-179.
[7] T Martin and J Idier. Estimating a conductivity distribution via a FEM-based nonlinear Bayesian method. [J]. Eur. Phys., 1998, 4:87-91.
[8] MT Clay and TC Ferree. Weighted regularization in electrical impedance tomography with applications to acute cerebral stroke. [J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2002, 21(6): 629-637.
[9] ET Chung, TF Chan, XC Tai. Electrical impedance tomography using level set representation and total variational regularization. [J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2005, 25:357–372.
[10] BS Kim, KY Kim, TJ Kao, et al. Dynamic electrical impedance imaging of a chest phantom using the Kalman filter. [J]. Phys. Meas., 2006, 27:81-91.
[11] R Olmi, M Bini, S Mantetta, et al. EIT reconstruction of static images by a genetic algorithm approach. [J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2006, 2(1):454-465.
[12] A Borsic, BM Graham, A Adler, et al. Total variation regularization in electrical impedance tomography. [EB/OL]. http://eprints.ma.man.ac.uk/813/ , 2007.
[13] A Adler, T Dai and W Lionheart. Temporal image reconstruction in electrical impedance tomography. [J]. Phys. Meas., 2007, 28:1-11.
[14] WR Fan and HX Wang. Maximum entropy regularization method for electrical impedance tomography combined with a normalized sensitivity map. [J]. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 2010(21):277-283.
[15] YQ Li. A novelty dynamic image reconstruction algorithm in electrical impedance tomography based on Nachman theory. [J]. Information Technology and Applications (IFITA), 2010 International Forum, 2010, 2:118-120.
[16] Q Wang and HX Wang. Image reconstruction based on expectation maximization method for electrical impedance tomography. [J]. Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST), 2011 IEEE International Conference, 2011:50-54.
[17] M Abbasi and A Naghsh-Nikchi. Precise two-dimensional D-bar reconstructions of human chest and phantom tank via sinc-convolution algorithm. [EB/OL]. http://www.biomedical-engineering-online.com/content/11/1/34/abstract , 2012.
[18] MX Tang, XZ Dong, MX Qing, et al. Electrical impedance tomography reconstruction algorithm based on general inversion theory and finite element method. [J]. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., 1998, 36:395-398.
[19] Xu C H, Dai M, You F S, Shi X T, Fu F, Liu R G and Dong X Z. An optimized strategy for real-time hemorrhage monitoring with electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. , 2011;32: 585-598.
[20] 劉國強. 醫學電磁成像. 北京: 科學出版社, 2006.

