基本介紹
技術簡介,計算公式,套用,代碼實現,
技術簡介
計算公式
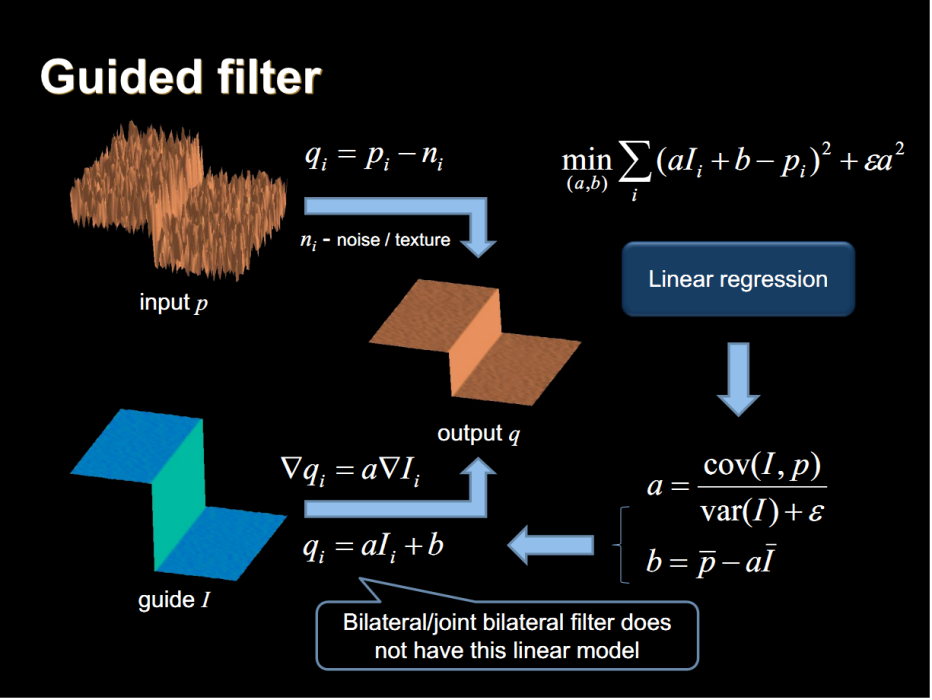
記引導圖(導向圖)為G,輸入圖像為X,輸出圖像為Y,導向圖濾波的目標就是使得原始的輸入和輸出儘可能相同,同時紋理部分與引導圖G相似。
對於目標1:輸入圖像X和輸出圖像Y儘可能相似,可以用公式描述為:

對於目標2:輸出圖像Y的紋理和引導圖G儘可能相似,用公式描述為:

上式中如果Y為單通道圖像,G為多通道,那么a為一個向量;如果Y和G通道數相同,那么a為標量或者對角矩陣。顯然,a的值越小,最後的輸出圖像也就越平滑。
對於目標2,可以對等式兩邊取定積分,從而得到:

下面就導向圖G和輸入圖X分兩種情況進行討論。
導向圖濾波
1. G為3通道,X為單通道
由於上式只是一個局部線性模型,因此兩個係數其實是一個與位置有關的變數。為了確定其值,考慮一個小視窗 ,使得視窗內的像素同時滿足上面兩個條件,可以將上式帶入第一個式子中得到目標函式(為了防止a過大,添加了一個懲罰項):
,使得視窗內的像素同時滿足上面兩個條件,可以將上式帶入第一個式子中得到目標函式(為了防止a過大,添加了一個懲罰項):


對兩個參數求偏導數得到:


由此可以解得:


上式取平均值操作都是在對應的視窗 中進行的。
中進行的。

2. G和X通道數相同
對於G和X通道數相同的情形,只需要考慮二者均為單通道的情況即可,多通道的情況可以分別進行單通道處理。具體過程與上面的類似,這裡直接給出最後的結果:


套用
1. 保邊圖像平滑
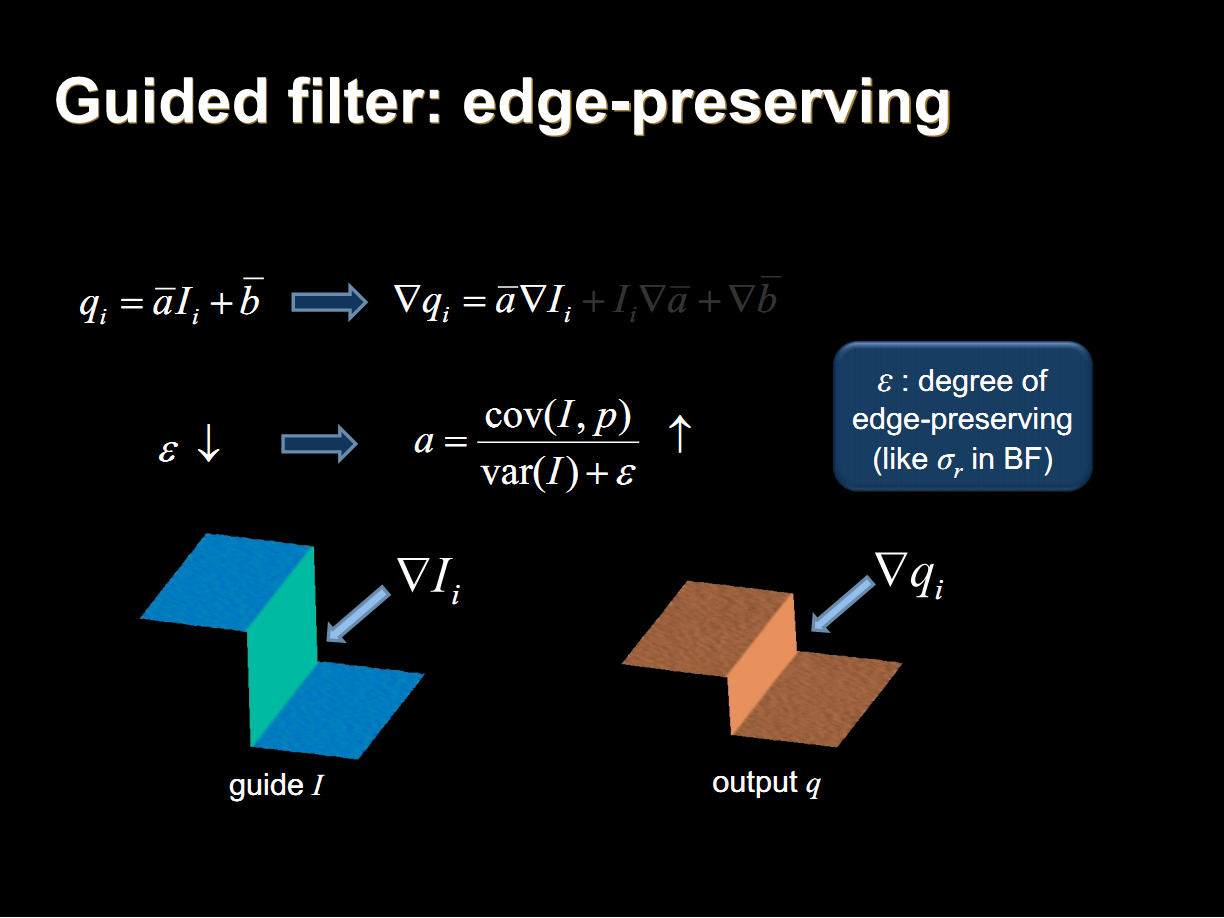
當引導圖G與輸入圖P為同一個圖像的時候,導向圖濾波的效果與雙邊濾波的效果類似,但是不同於雙邊濾波的是,導向圖濾波可以很容易設計一個與濾波半徑無關的最佳化算法。其中視窗半徑為平滑半徑,參數 為平滑項參數,其值越大平滑的越明顯。
為平滑項參數,其值越大平滑的越明顯。


保邊圖像平滑
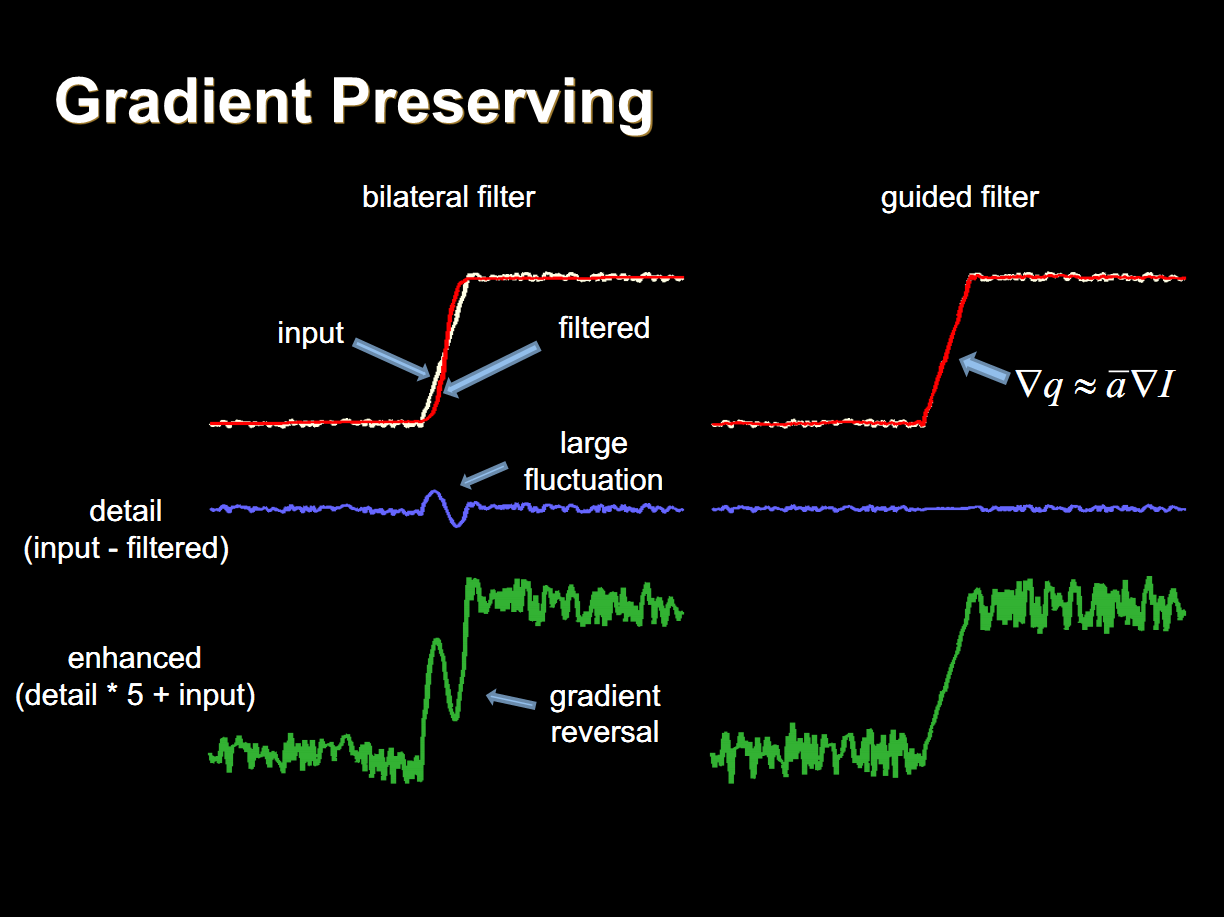
保邊圖像平滑
2. 摳圖
當輸入圖P為一個初始的mask圖像時,導向圖濾波的效果類似於摳圖算法,其中視窗半徑為摳圖的半徑,參數 為平滑項。
為平滑項。
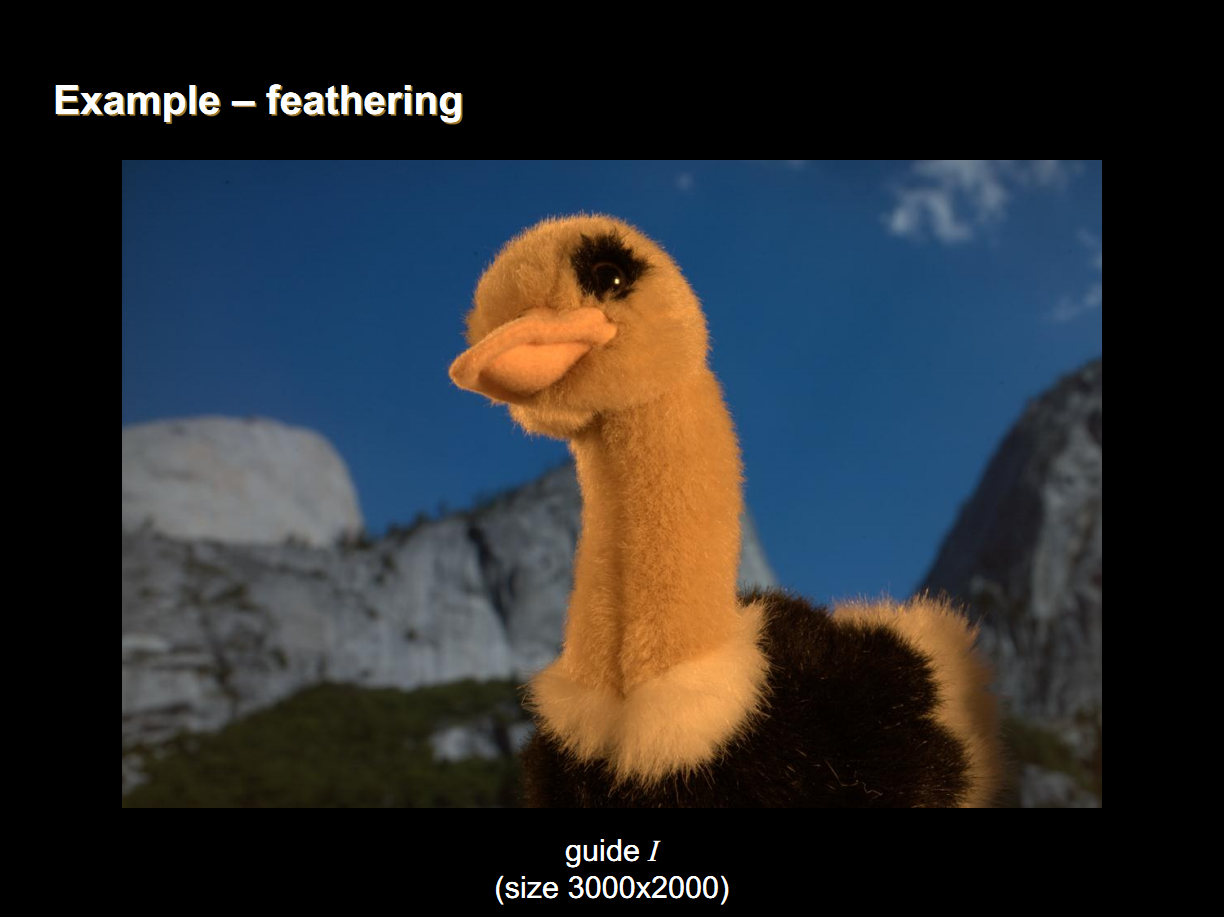


摳圖
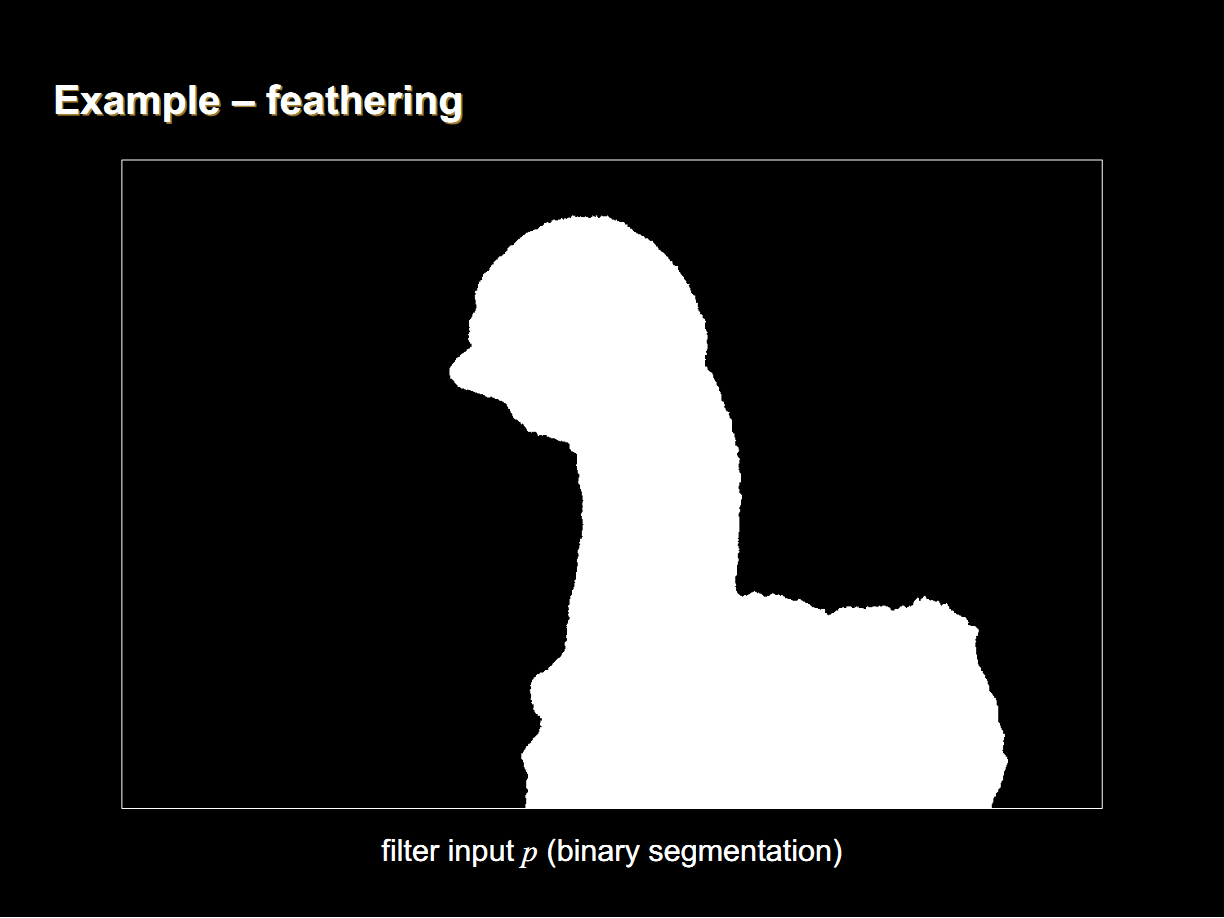

摳圖

摳圖
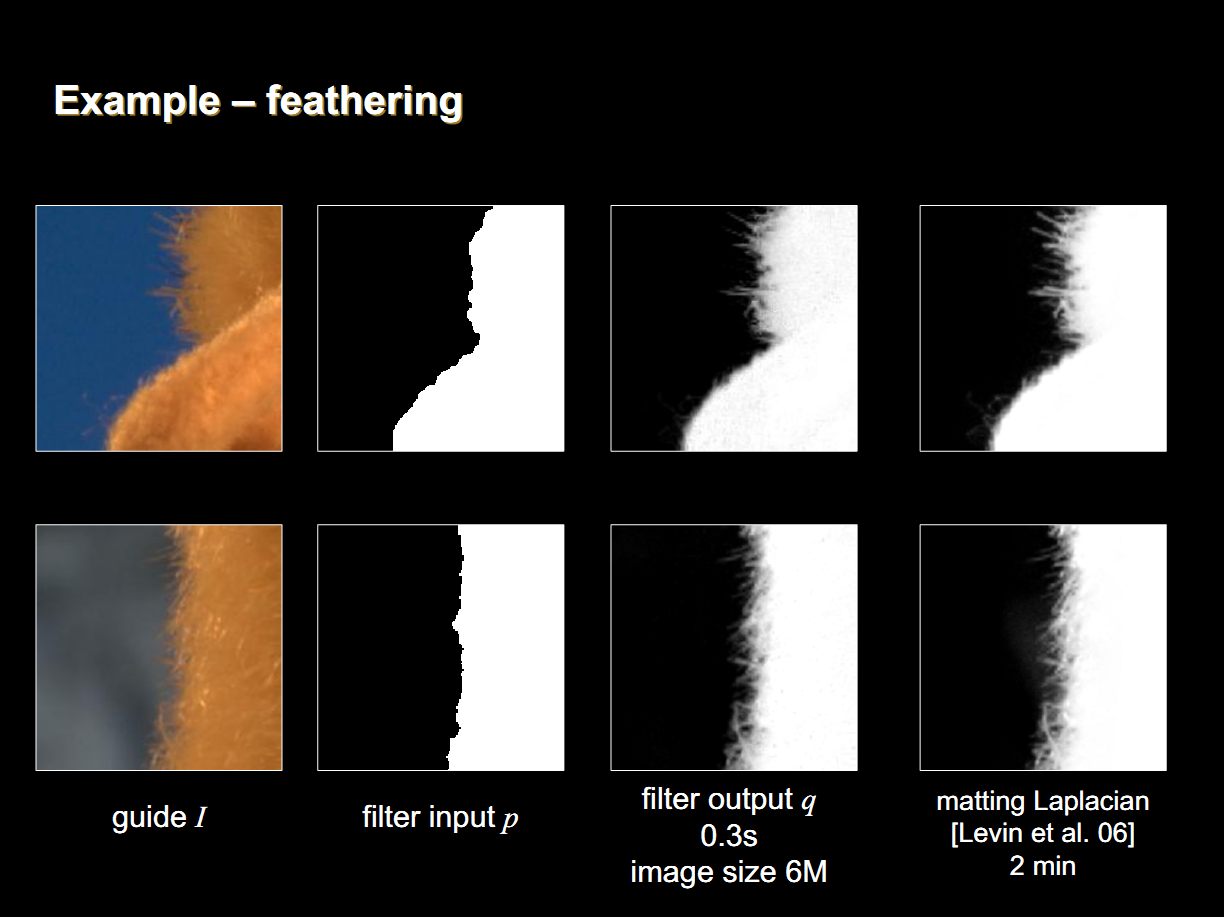
摳圖
代碼實現
不難看出,導向圖濾波的主要步驟就兩個,計算每個公式中的各種平均值,然後根據平均值計算出 和
和 ,最後根據
,最後根據 得到輸出圖像。
得到輸出圖像。



計算平均值可以通過積分圖高效的實現,matlab代碼如下:
矩形濾波代碼(計算視窗平均值)
function imDst = boxfilter(imSrc, r)
% BOXFILTER O(1) time box filtering using cumulative sum
%
% - Definition imDst(x, y)=sum(sum(imSrc(x-r:x+r,y-r:y+r)));
% - Running time independent of r;
% - Equivalent to the function: colfilt(imSrc, [2*r+1, 2*r+1], 'sliding', @sum);
% - But much faster.
[hei, wid] = size(imSrc);
imDst = zeros(size(imSrc));
%cumulative sum over Y axis
imCum = cumsum(imSrc, 1);
%difference over Y axis
imDst(1:r+1, :) = imCum(1+r:2*r+1, :);
imDst(r+2:hei-r, :) = imCum(2*r+2:hei, :) - imCum(1:hei-2*r-1, :);
imDst(hei-r+1:hei, :) = repmat(imCum(hei, :), [r, 1]) - imCum(hei-2*r:hei-r-1, :);
%cumulative sum over X axis
imCum = cumsum(imDst, 2);
%difference over Y axis
imDst(:, 1:r+1) = imCum(:, 1+r:2*r+1);
imDst(:, r+2:wid-r) = imCum(:, 2*r+2:wid) - imCum(:, 1:wid-2*r-1);
imDst(:, wid-r+1:wid) = repmat(imCum(:, wid), [1, r]) - imCum(:, wid-2*r:wid-r-1);
end